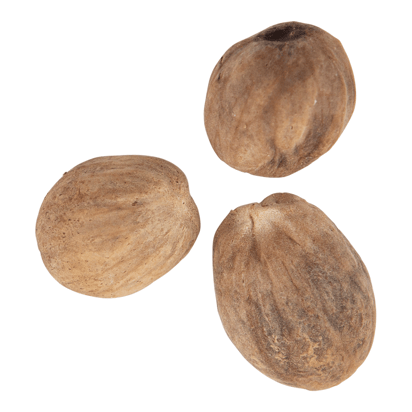
Nutmeg: Important Facts, Health Benefits, and Recipes
Explore the versatile world of nutmeg with our comprehensive guide, covering its origins, health benefits, culinary uses, and storage tips.

Nutritional Facts
1 tsp
Amount per serving
Calories
11.6
Carbohydrates
1.1 g
Fat
0.8 g
Protein
0.1 g
Saturated Fat
0.6 g
Sodium
0.4 mg
Fiber
0.5 g
Sugar
0.1 g
Best Nutmeg Recipes
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
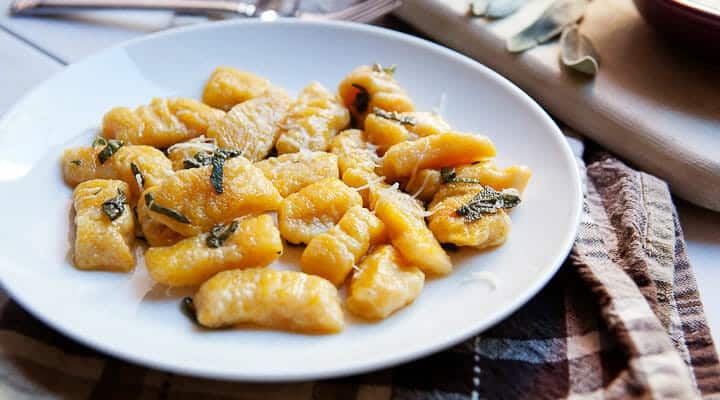
![Butternut Squash Gnocchi Image]()
-
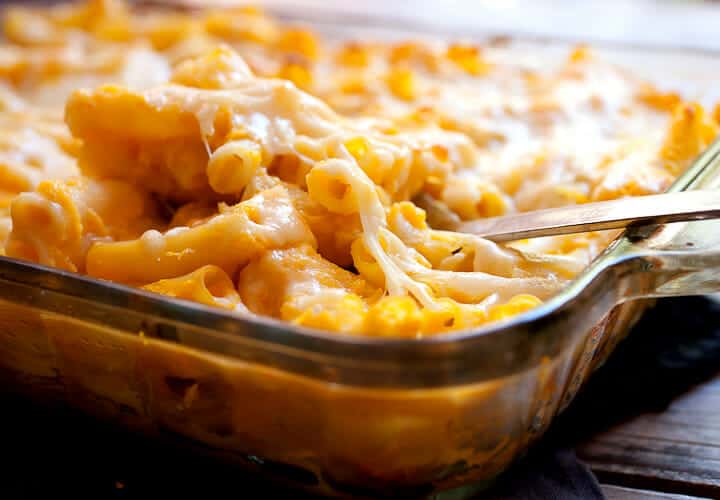
![Butternut Squash Baked Ziti Image]()
-
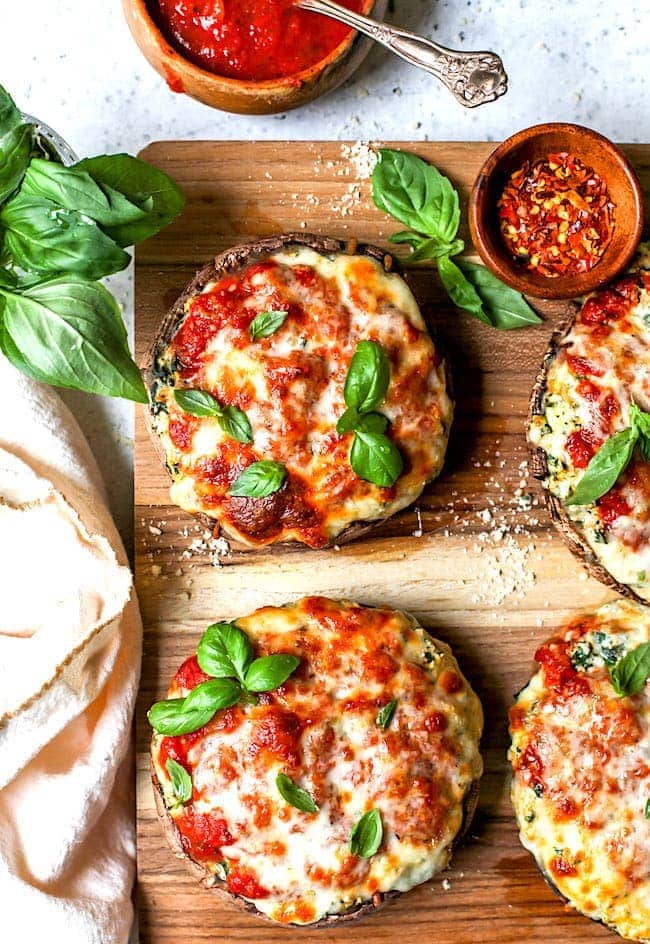
![Lasagna Stuffed Mushrooms Image]()
-
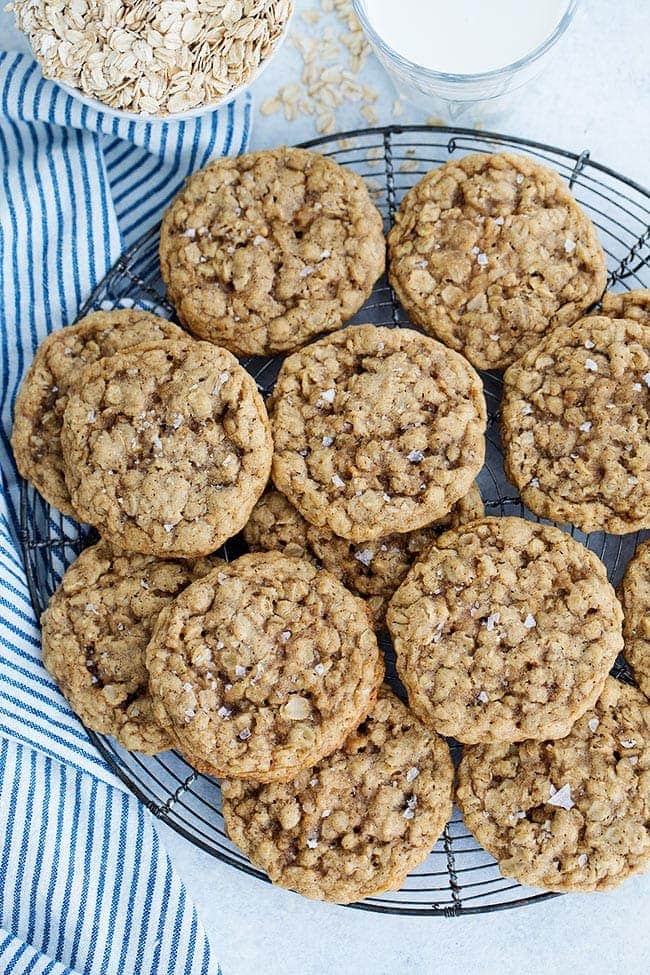
![Oatmeal Cookies Image]()
-
![Brown Butter Ginger Molasses Blondies Image]()
-
![Salted Caramel Pumpkin Pie Image]()
-
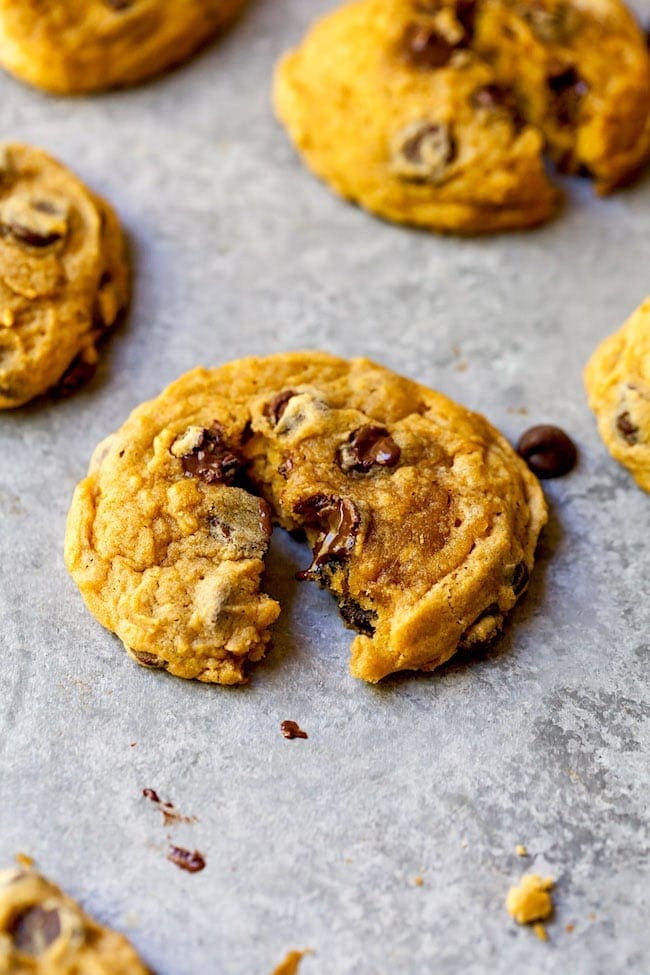
![Pumpkin Chocolate Chip Cookies Image]()
-
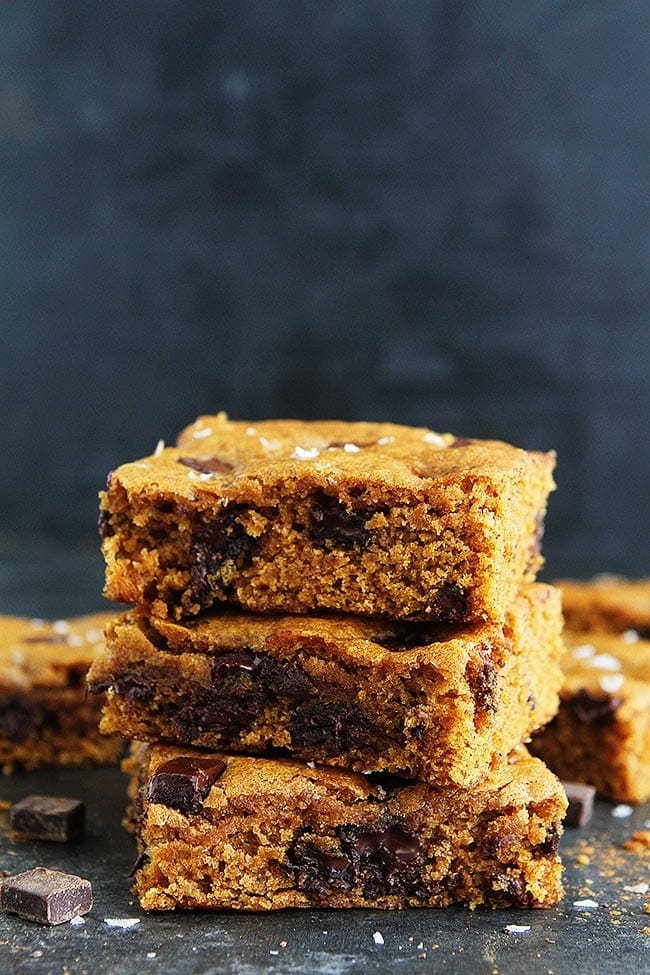
![Brown Butter Pumpkin Chocolate Chunk Bars Image]()
-
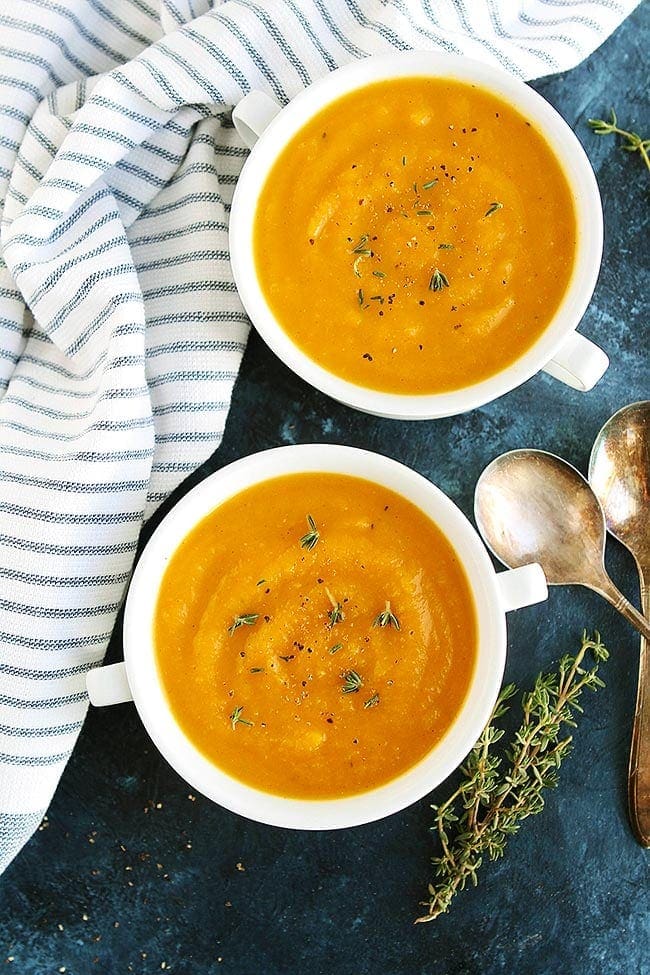
![Easy Butternut Squash Soup Image]()
-
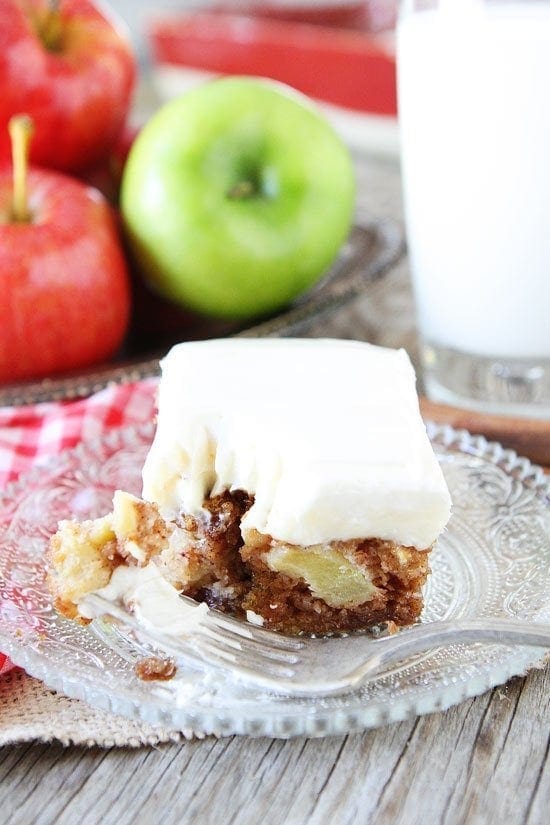
![Apple Cake with Cream Cheese Frosting Image]()
-
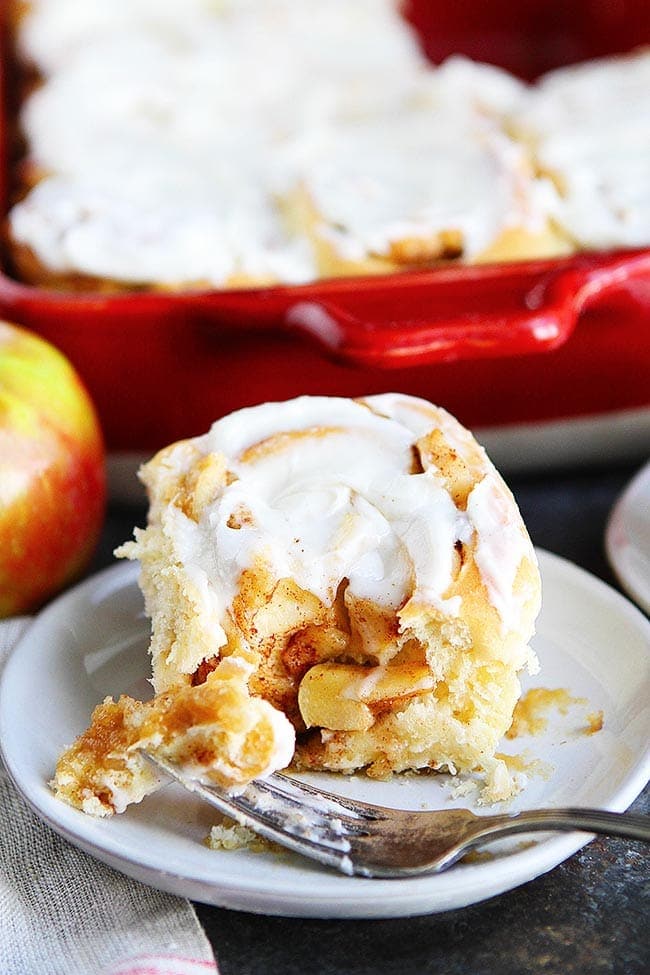
![Apple Cinnamon Rolls Image]()
-
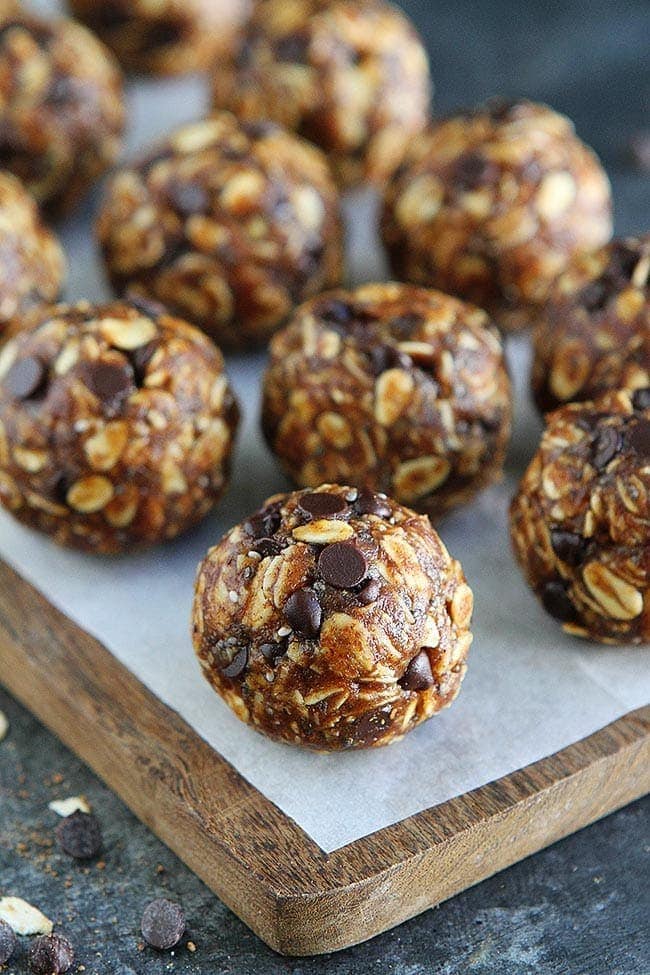
![Pumpkin Energy Balls Image]()
-
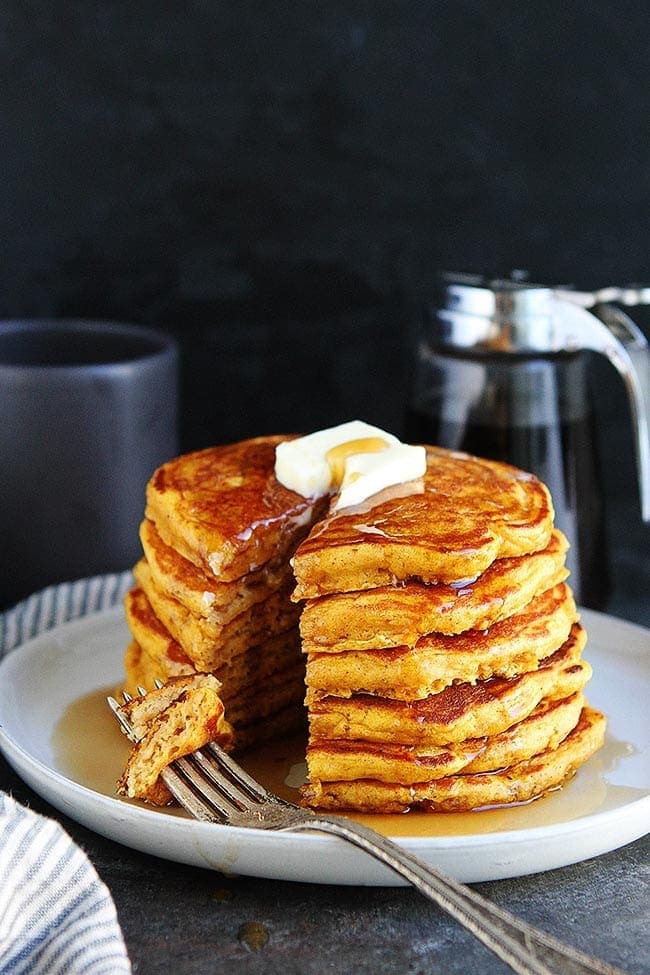
![Pumpkin Pancakes Image]()
-
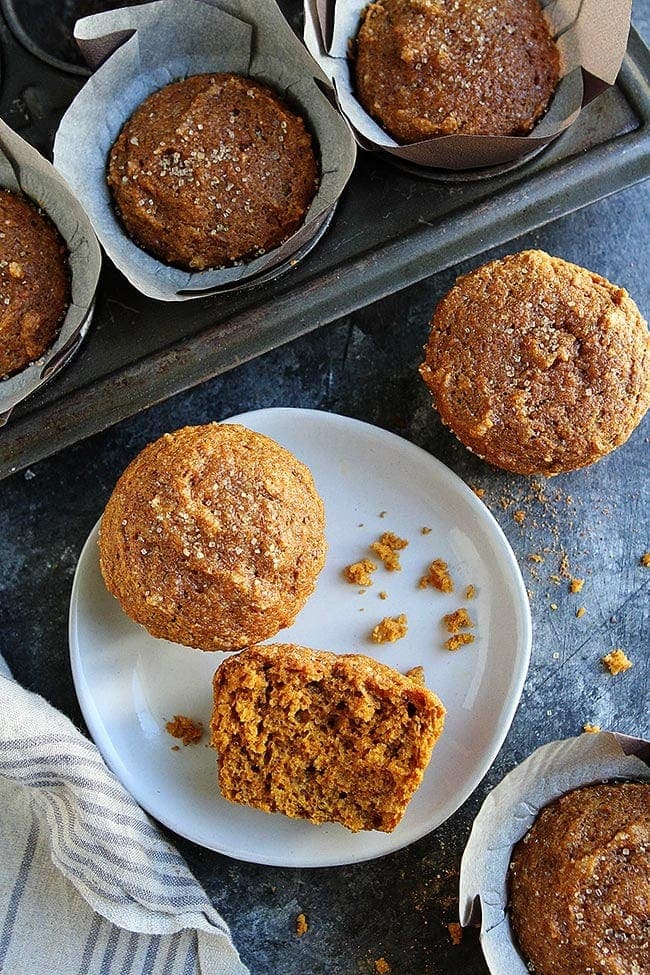
![Healthy Pumpkin Muffins Image]()
-
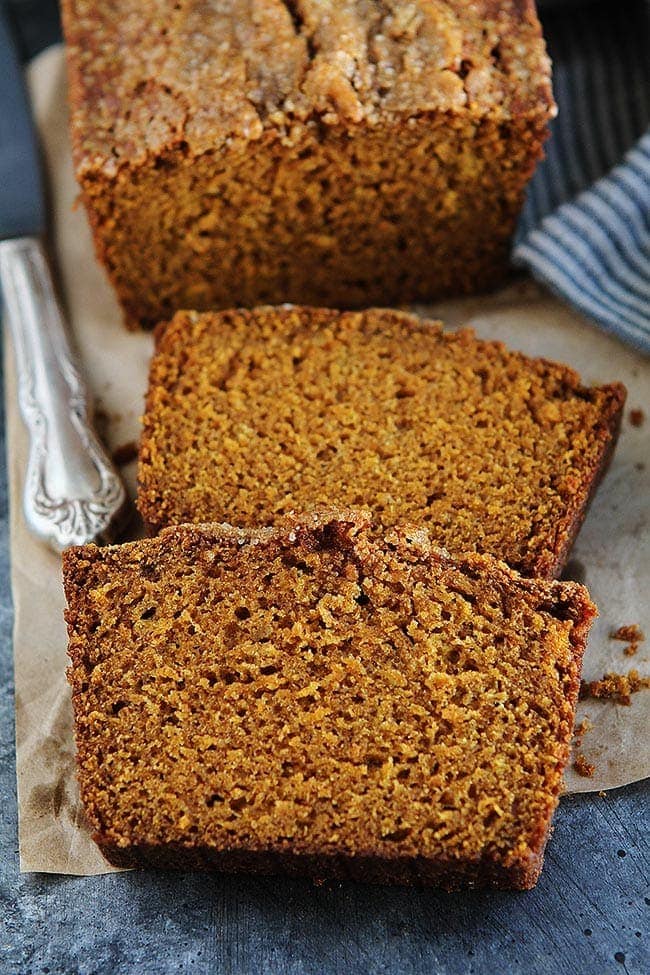
![Pumpkin Bread Image]()
-
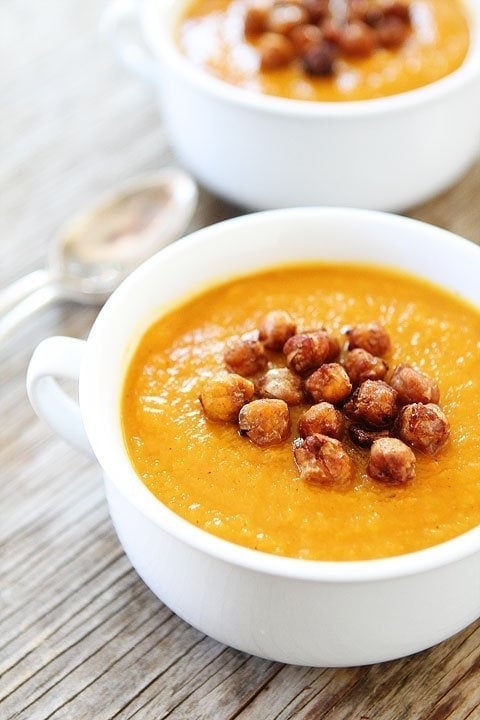
![Slow Cooker Butternut Squash Soup with Maple Roasted Chickpeas Image]()
-
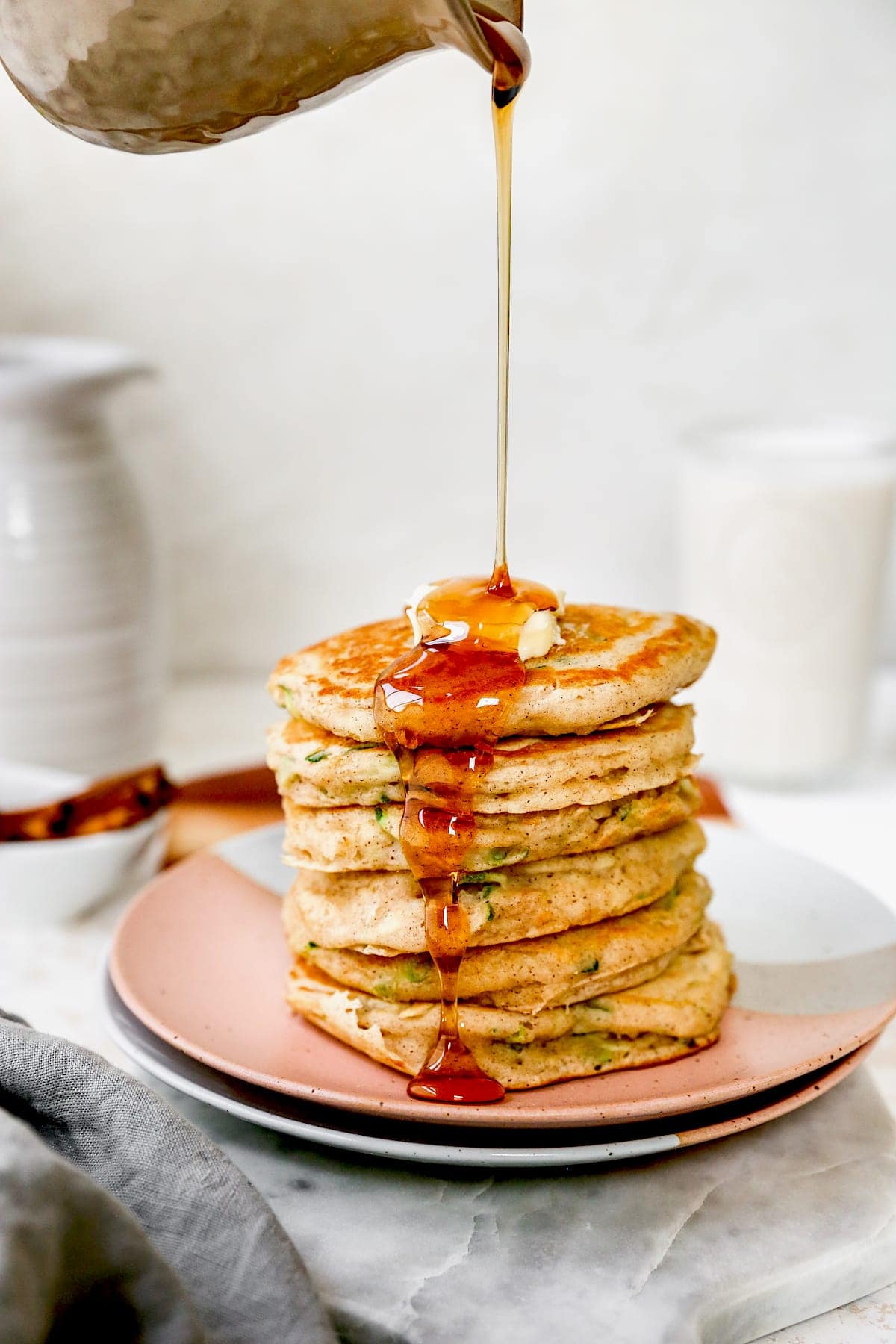
![Zucchini Pancakes Image]()
-
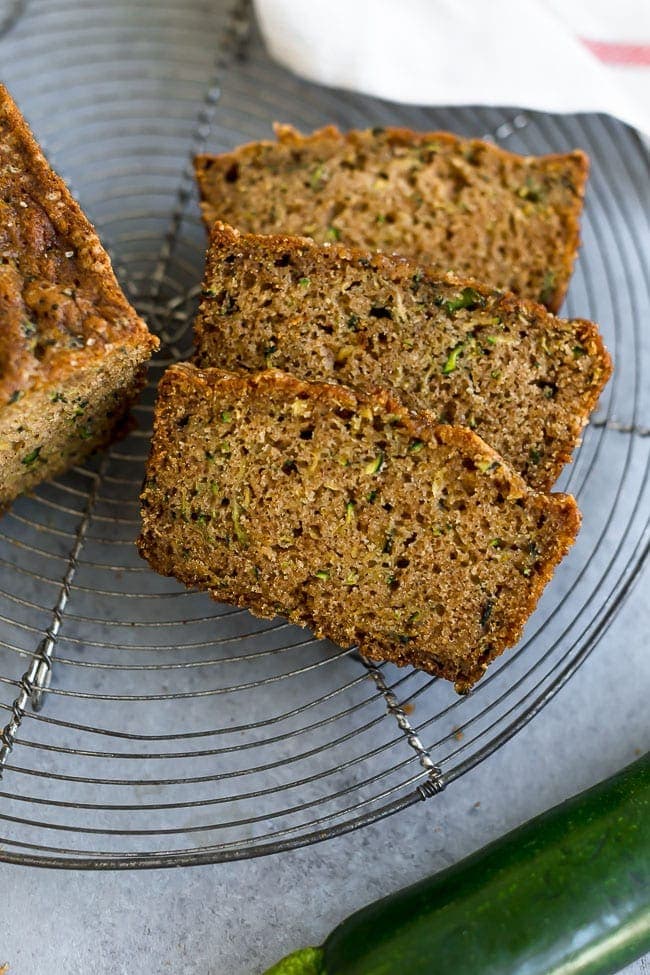
![Zucchini Bread Image]()
-
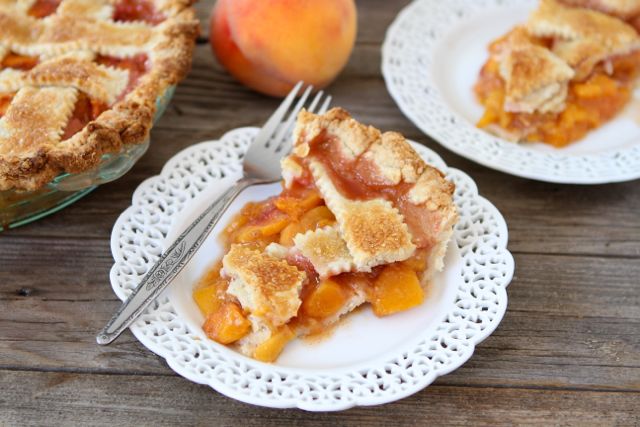
![Peach Pie Image]()
-
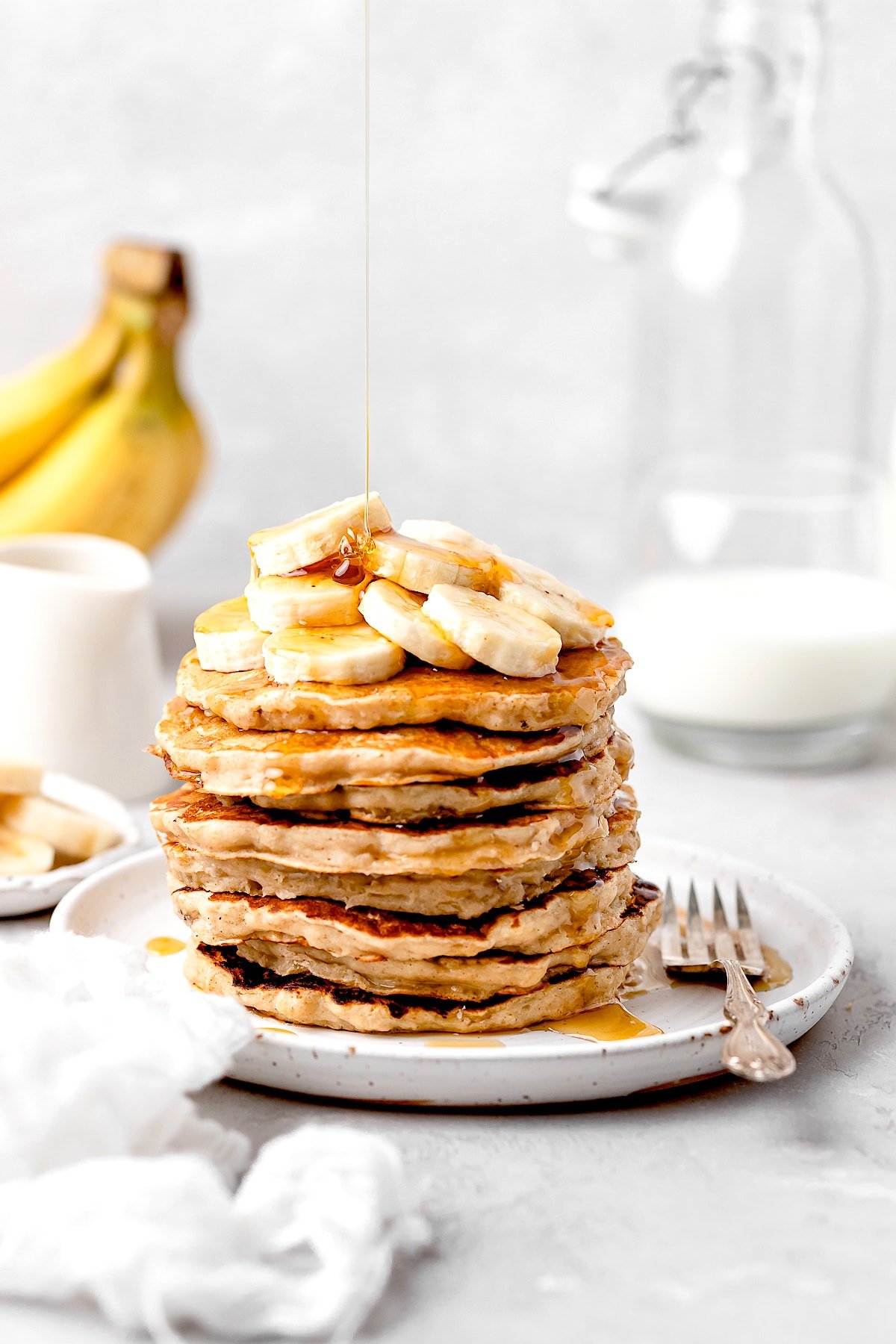
![Banana Pancakes Image]()
-
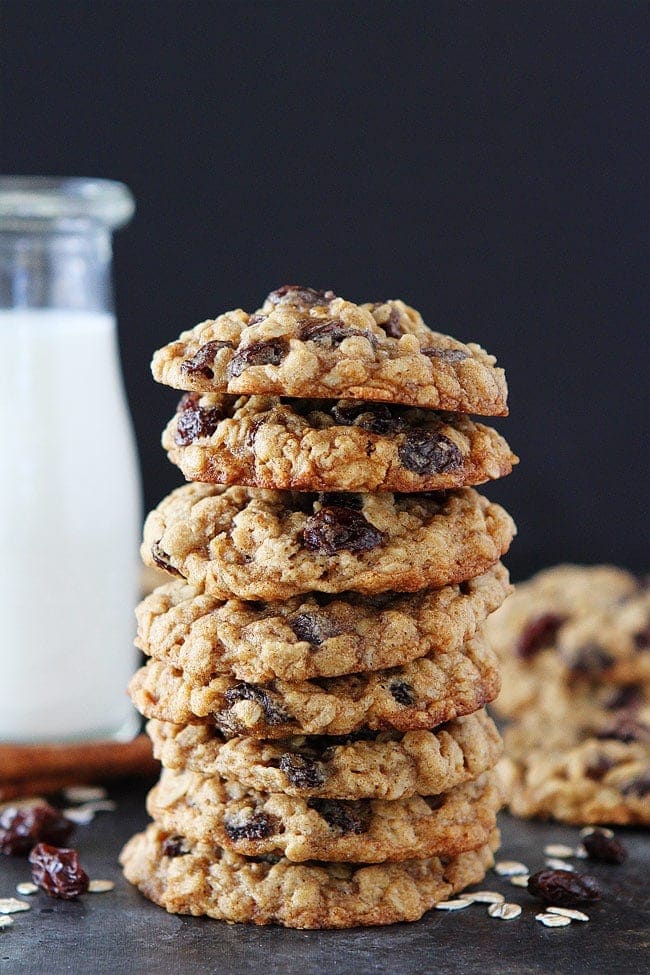
![Chewy Oatmeal Raisin Cookies Image]()
-
![Deep Dish Gingerbread Truffle Cookies Image]()
-
![Cinnamon Streusel Baked Apples Image]()
-
![Pumpkin Cream Cheese Muffins Image]()
-
![Eggnog Bread Image]()
-
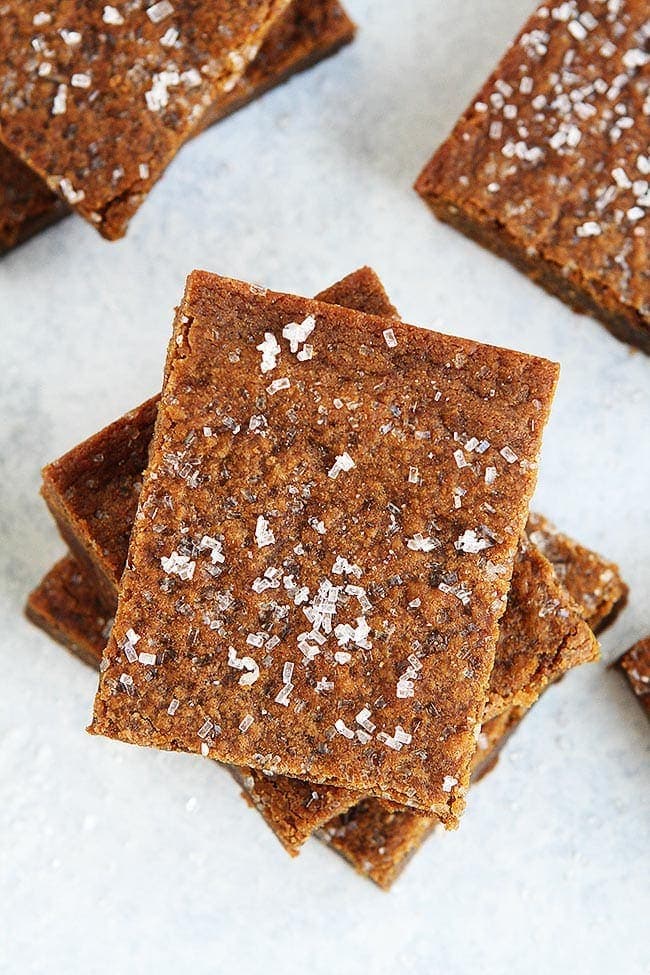
![Soft Gingersnap Cookies Image]()
-
![Sweet Potato, Kale, and Goat Cheese Frittata Image]()
-
![Pumpkin Coconut Chocolate Chip Muffins Image]()
-
![Gingersnap Sandwich Cookies with White Chocolate Filling Image]()
-
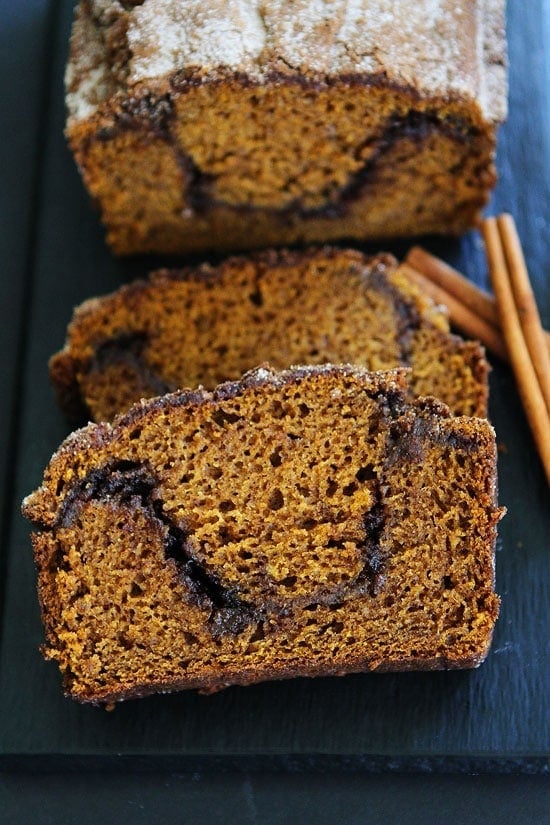
![Pumpkin Cinnamon Swirl Bread Image]()
-
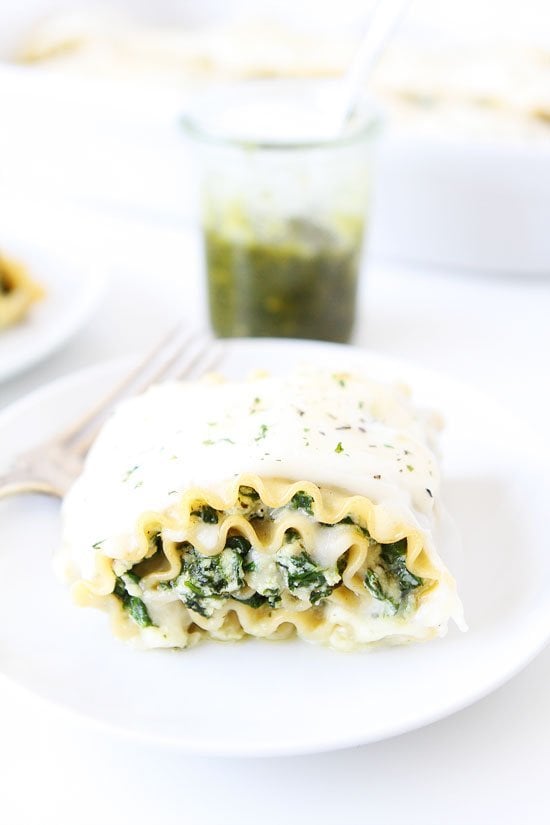
![Pesto Lasagna Roll Ups Image]()
-
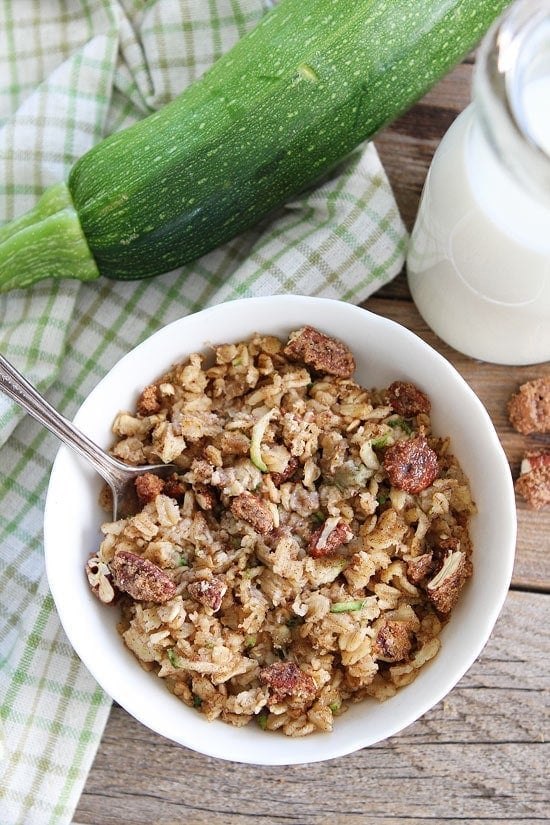
![Zucchini Bread Baked Oatmeal Image]()
-
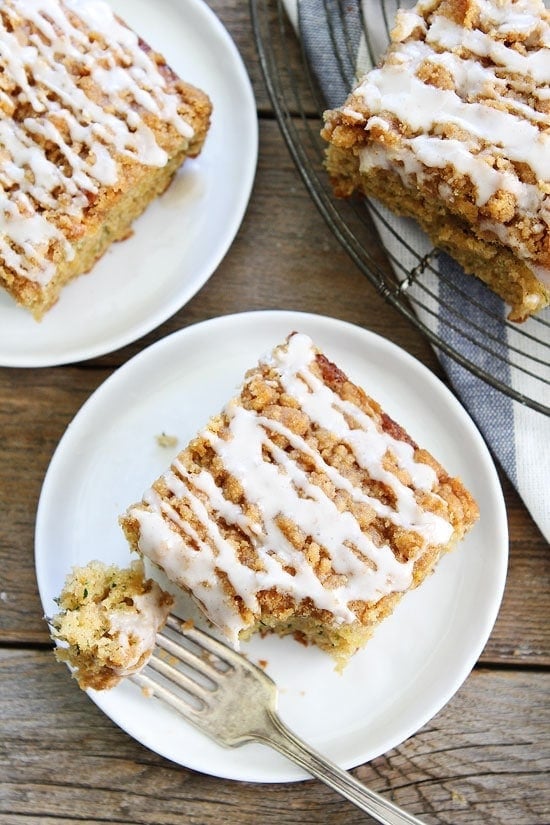
![Brown Butter Zucchini Coffee Cake Image]()
-
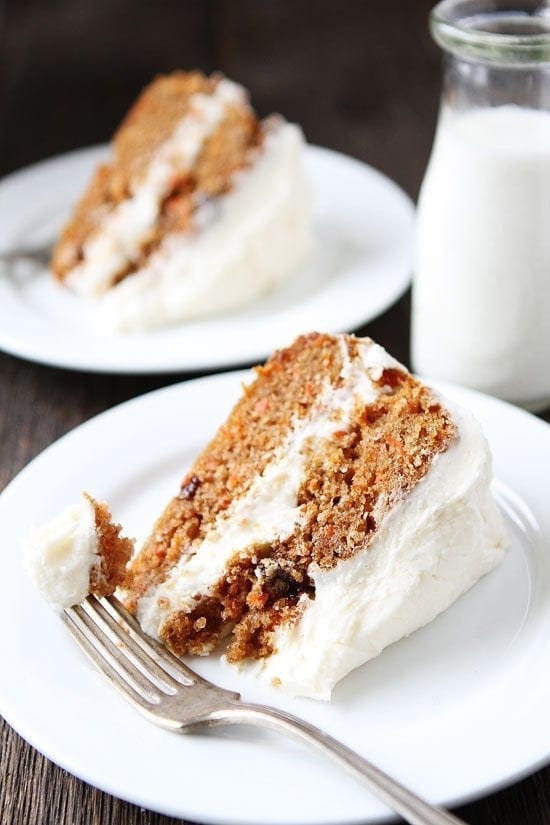
![Carrot Cake Image]()
-
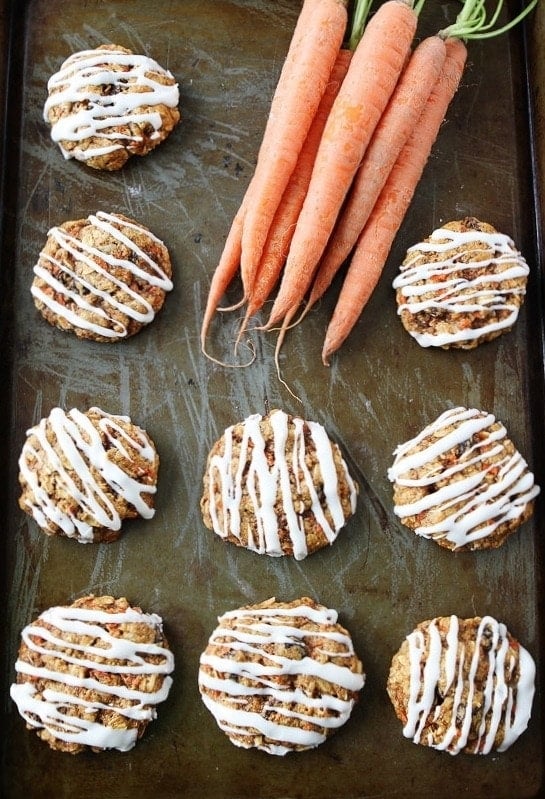
![Carrot Cake Oatmeal Cookies with Cream Cheese Glaze Image]()
-
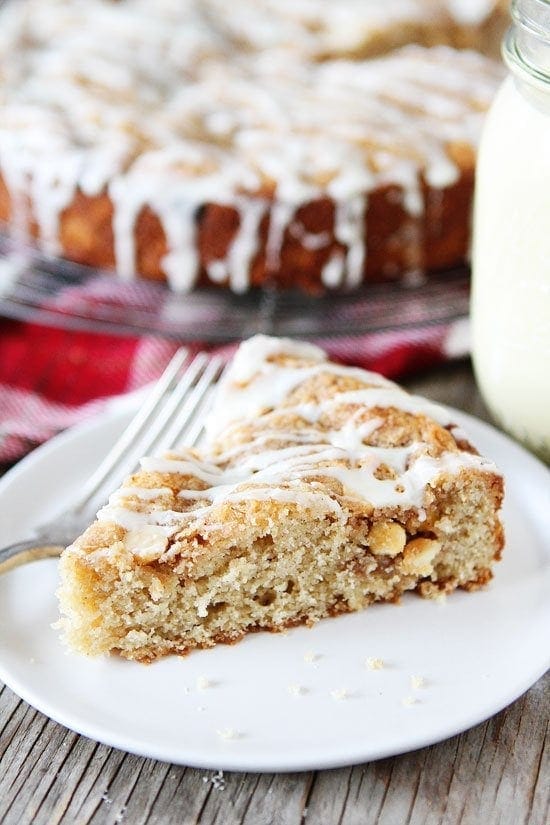
![Eggnog White Chocolate Streusel Cake Image]()
-
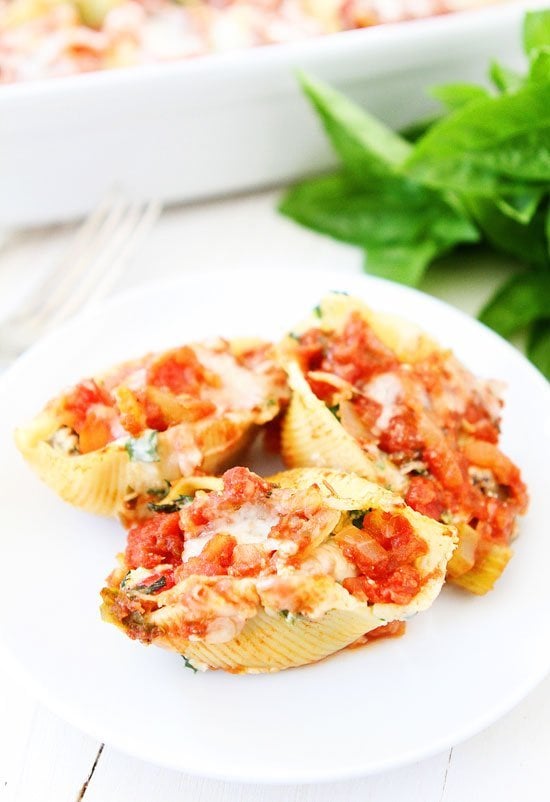
![Roasted Vegetable Stuffed Shells Image]()
-
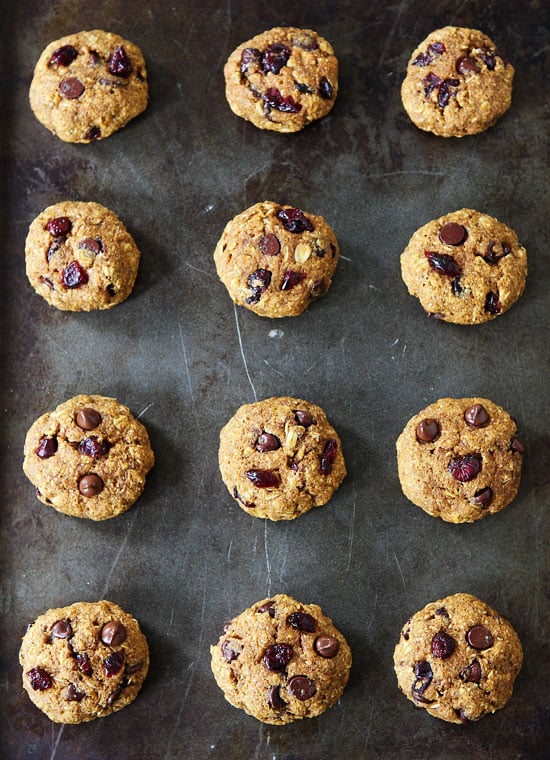
![Vegan Pumpkin Breakfast Cookies Image]()
-
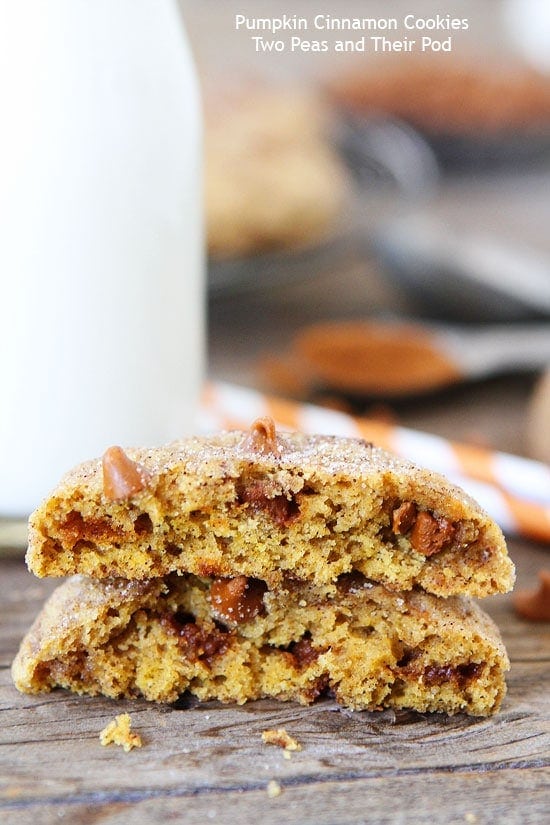
![Pumpkin Cinnamon Cookies Image]()
-
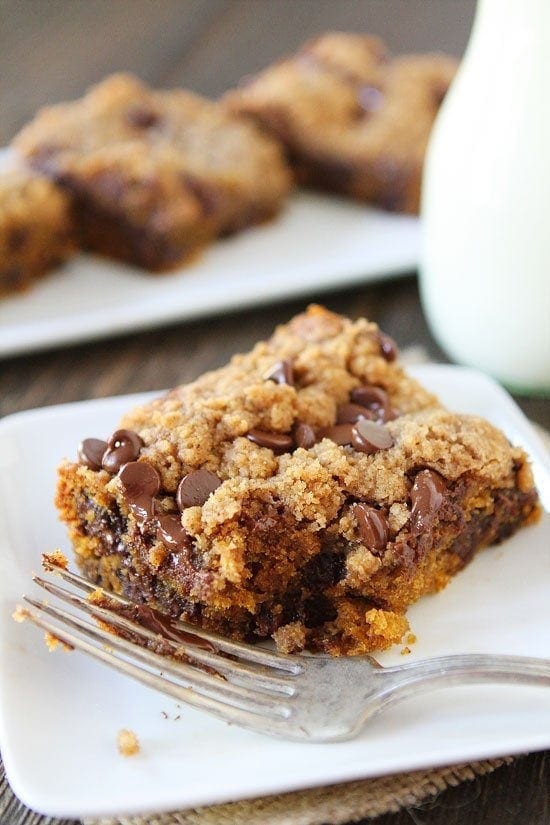
![Pumpkin Chocolate Chip Streusel Cake Image]()