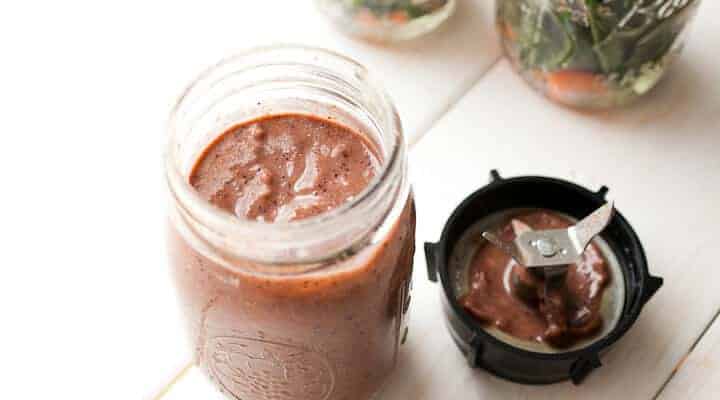Carrots: Important Facts, Health Benefits, and Recipes
Carrots are a crunchy root vegetable rich in antioxidants and beta carotene, known for their potential health benefits, such as supporting vision.

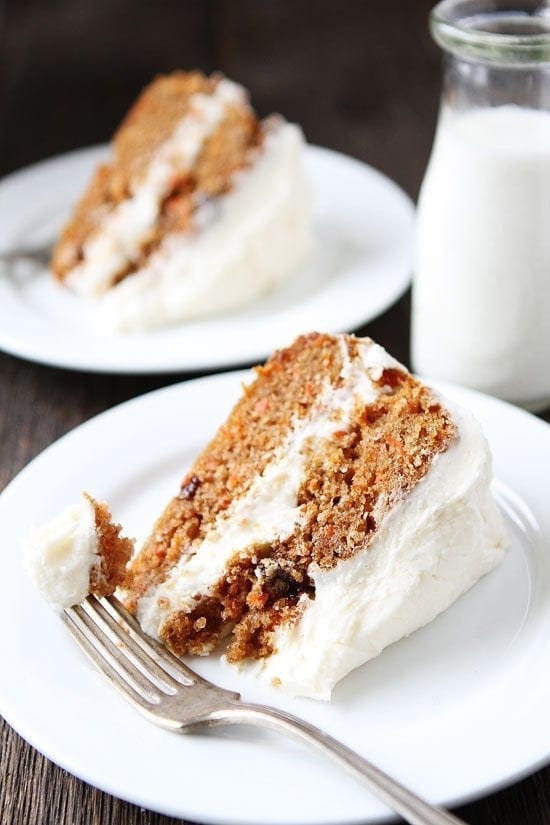
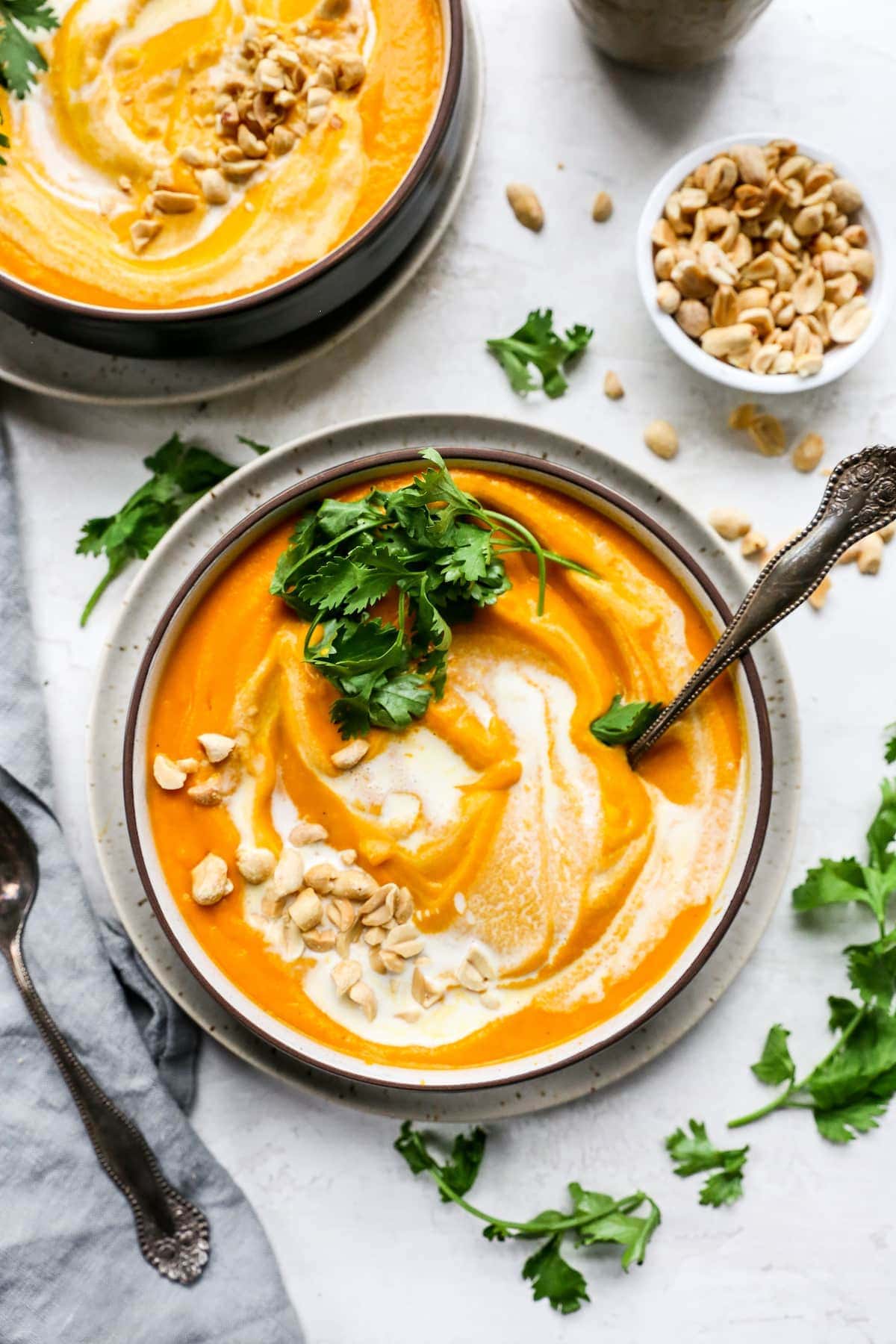
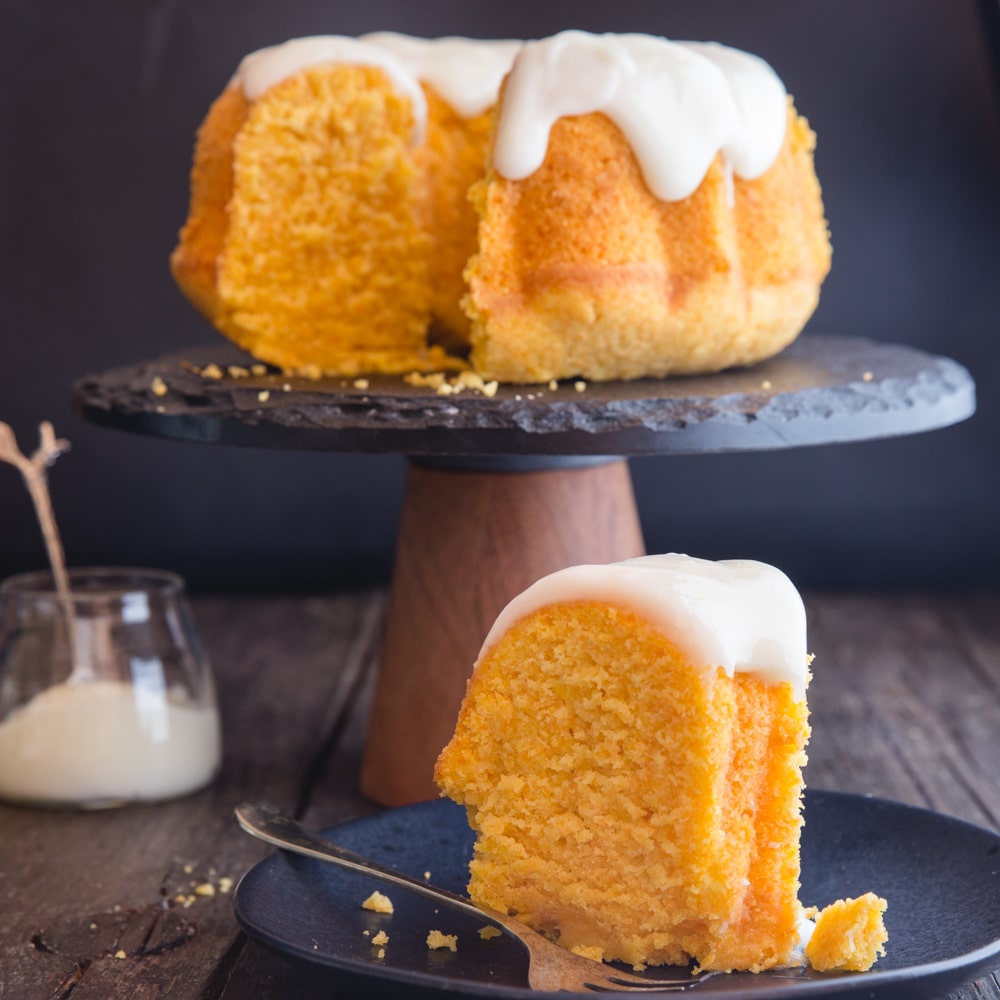
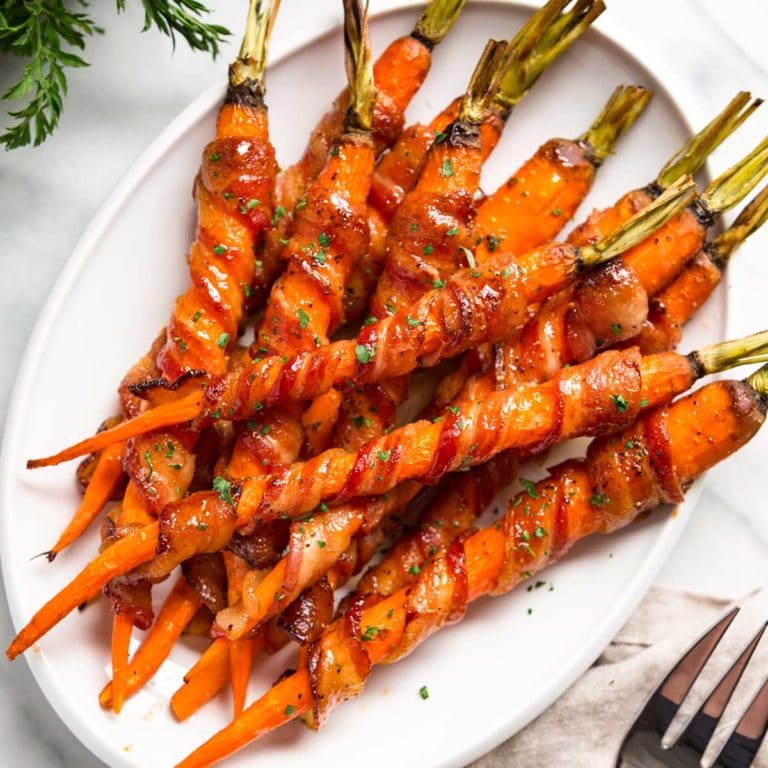
Best Carrots Recipes
-

-

-

-
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__serious_eats__seriouseats.com__recipes__images__2011__12__20111226-185245-finished-marinated-carrots-610-1-f964678e059b43eaadd3b37096c09651.jpg)
-

-

-

-

-
![Carrot Soufflé Image]()
-
![Carrot Top Pesto Recipe Image]()
-
![Mexican Pickled Carrots + Video Image]()
-
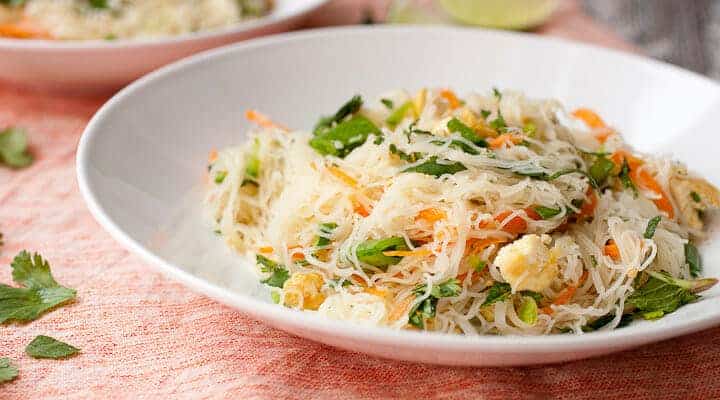
![Singapore Fried Rice Image]()
-
![Carrot Cake Ice Cream Recipe Image]()
-
![Tabbouleh with Cauliflower, Carrots, and Beets Recipe Image]()
-
![Stovetop Tzimmes With Carrots and Raisins Recipe Image]()
-
![Roasted Carrot Fries Image]()
-
![Eggplant Orzo Bake Image]()
-
![Mushroom Meatloaf Image]()
-
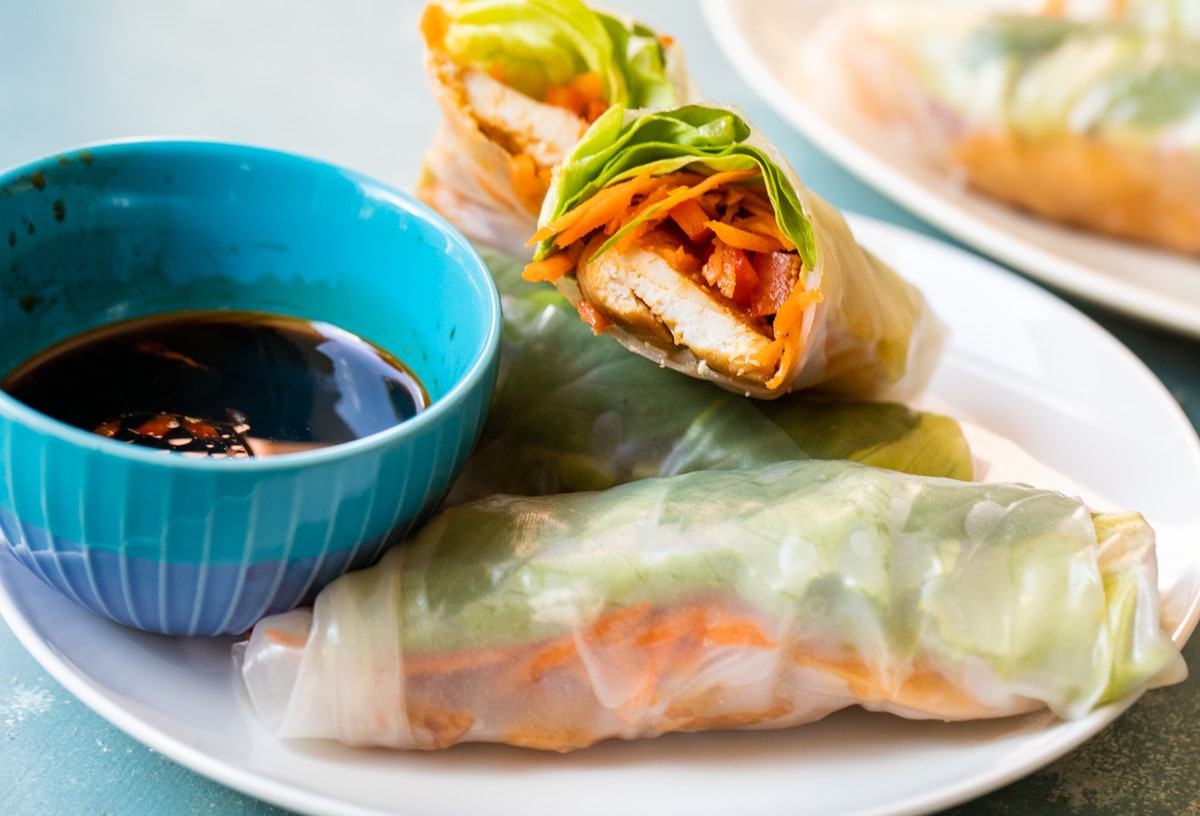
![Tempeh Spring Rolls Image]()
-
![Kid Friendly Chicken Ramen Soup Image]()
-
![Traditional Mole Sauce Image]()
-
![Slow Cooker Korean BBQ Tacos Image]()
-
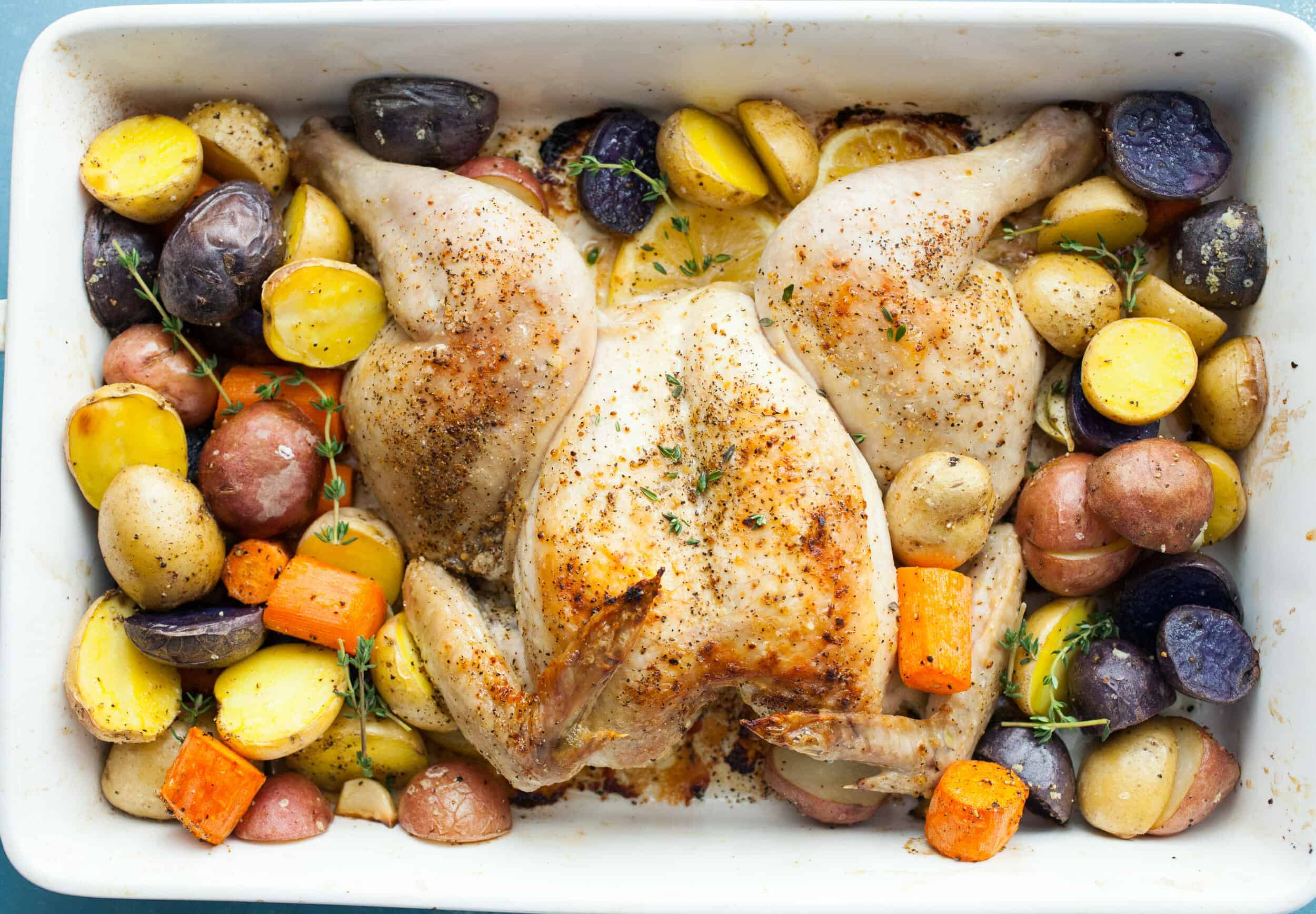
![Lemon Pepper Spatchcock Chicken Image]()
-
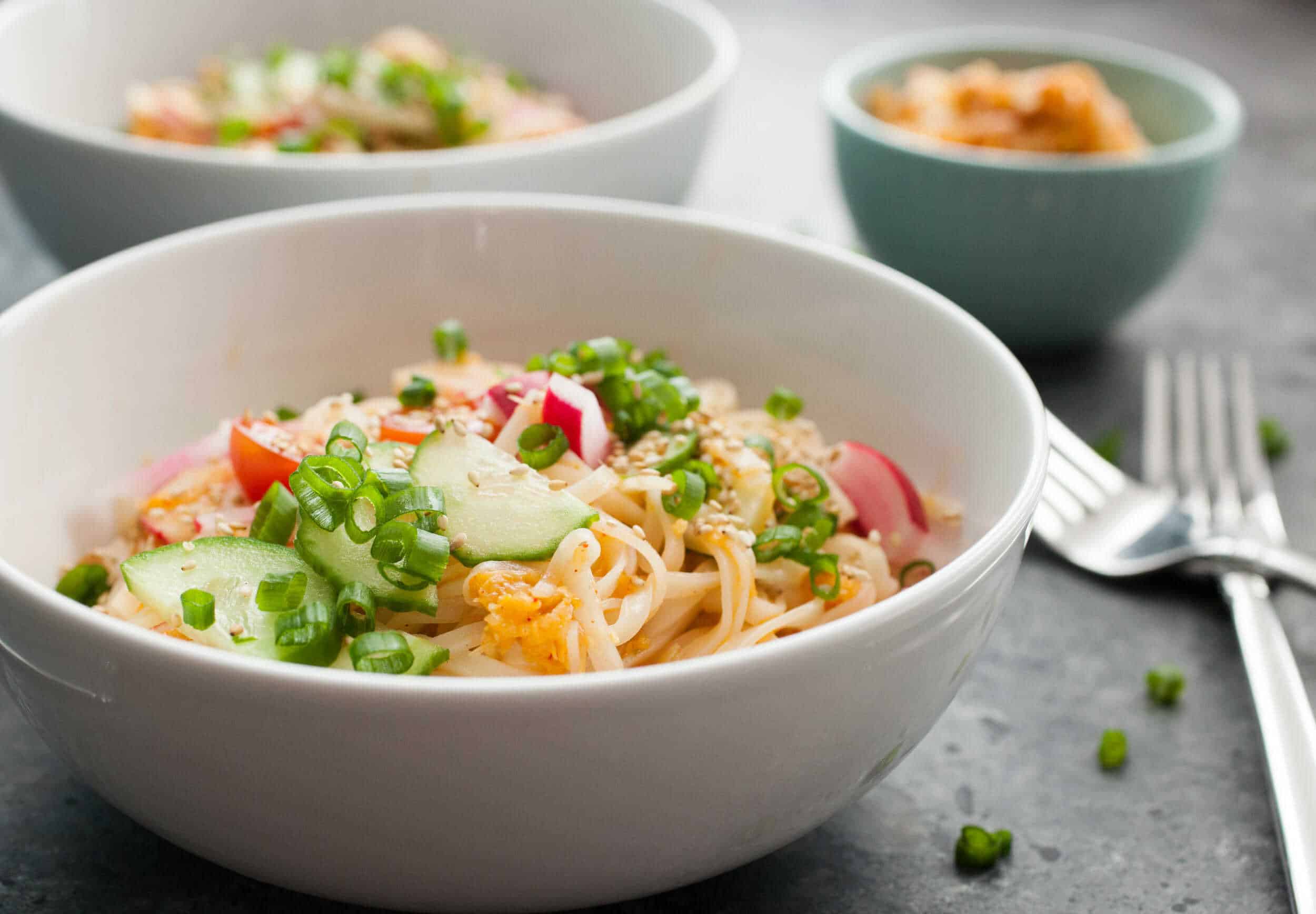
![Easy Kimchi Noodles Image]()
-
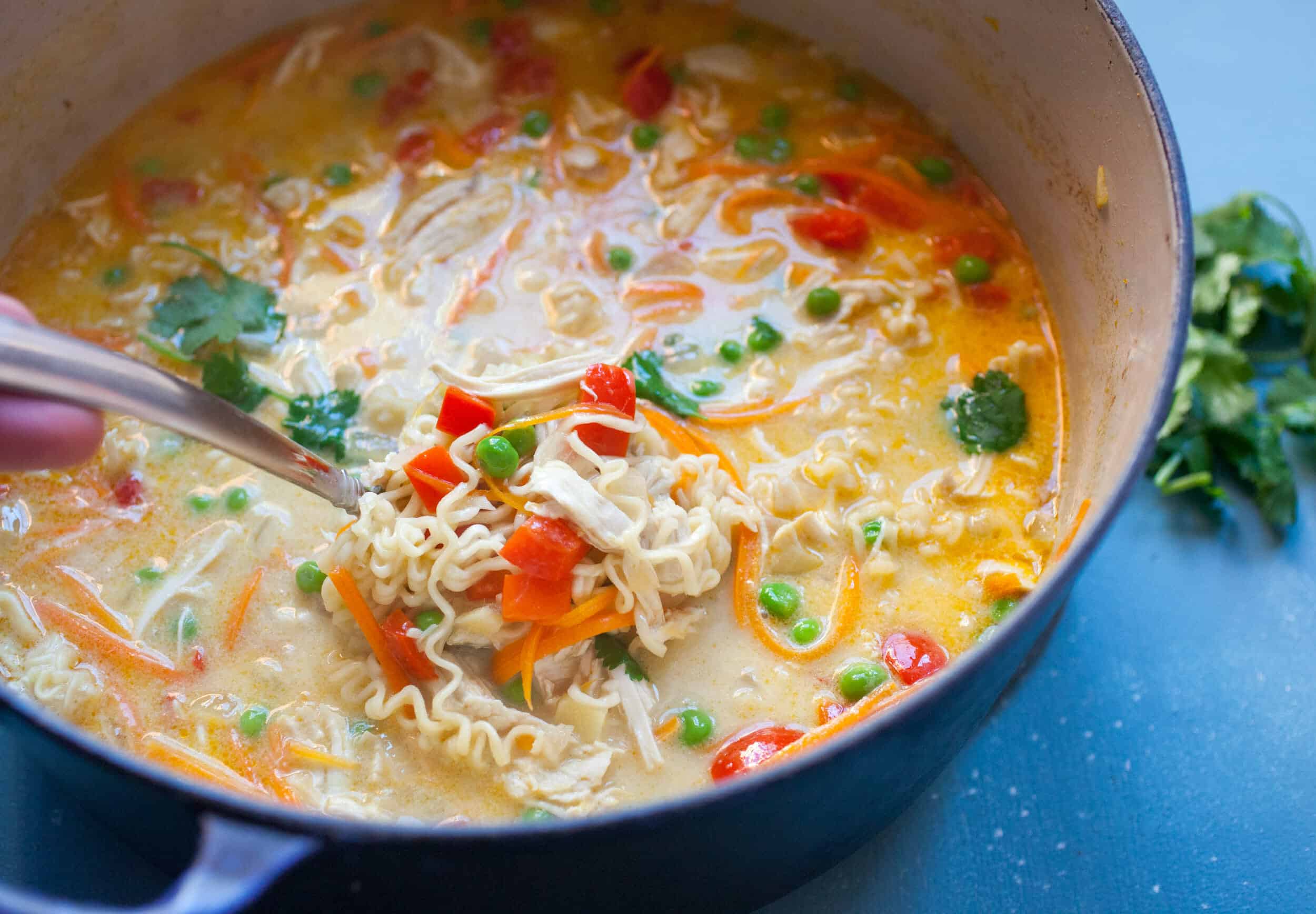
![Chicken and Stars Soup Image]()
-
![Rainbow Spring Rolls Image]()
-
![Grilled Fish Tacos Image]()
-
![Crispy Homemade Veggie Nuggets Image]()
-
![Sriracha Chicken Spring Rolls Image]()
-
![Peri Peri Chicken Image]()
-
![Mushroom and Chicken Soup Image]()
-
![Mason Jar Smoothies Image]()
-
![Cold Rice Noodle Salad with Crumbled Tofu Image]()
-
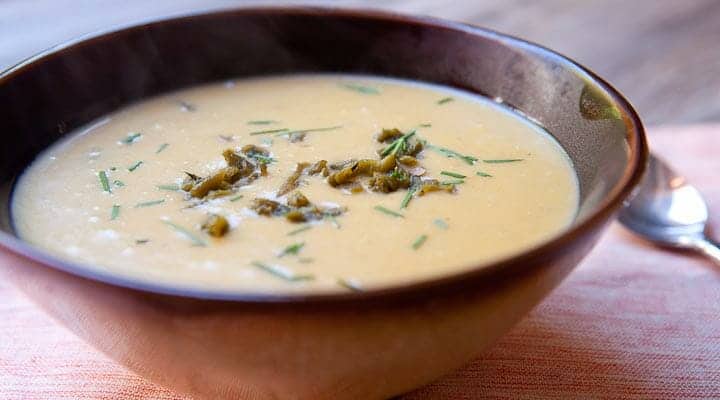
![Green Chile Cream of Potato Soup Image]()
-
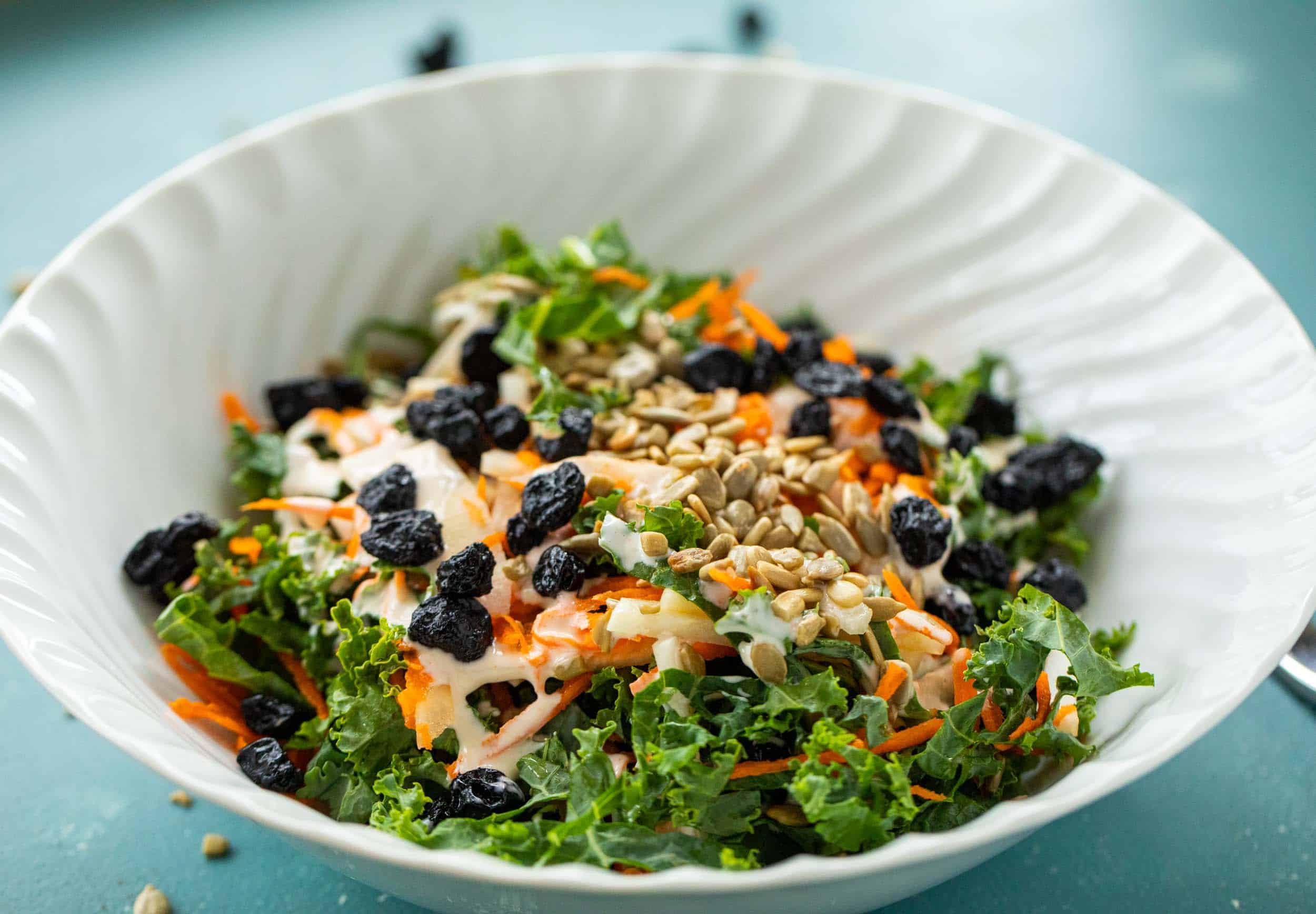
![Creamy Kale Slaw with Blueberries and Seeds Image]()
-
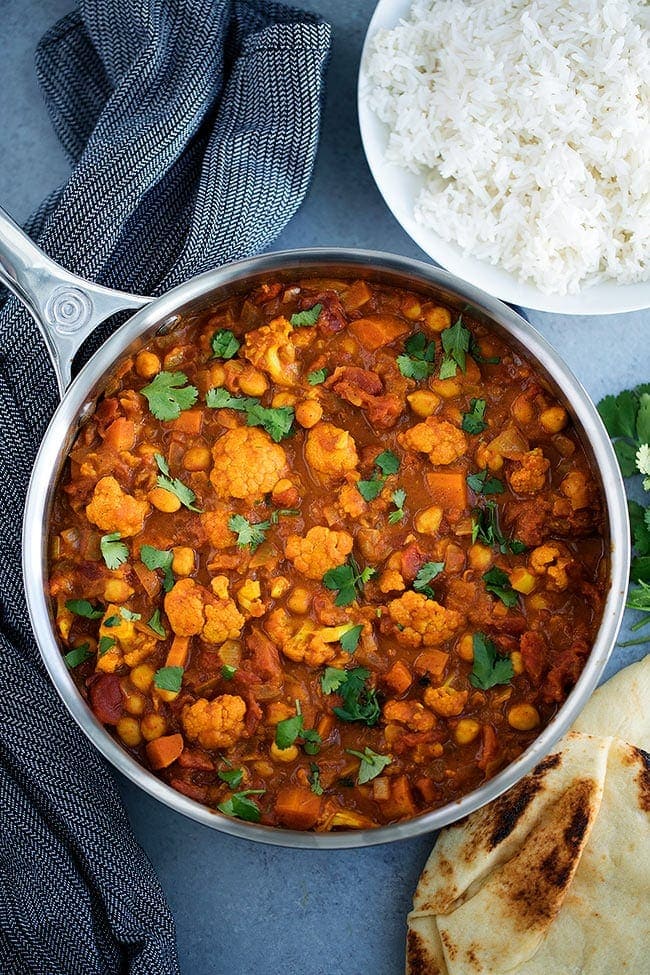
![Vegetarian Tikka Masala Image]()
-
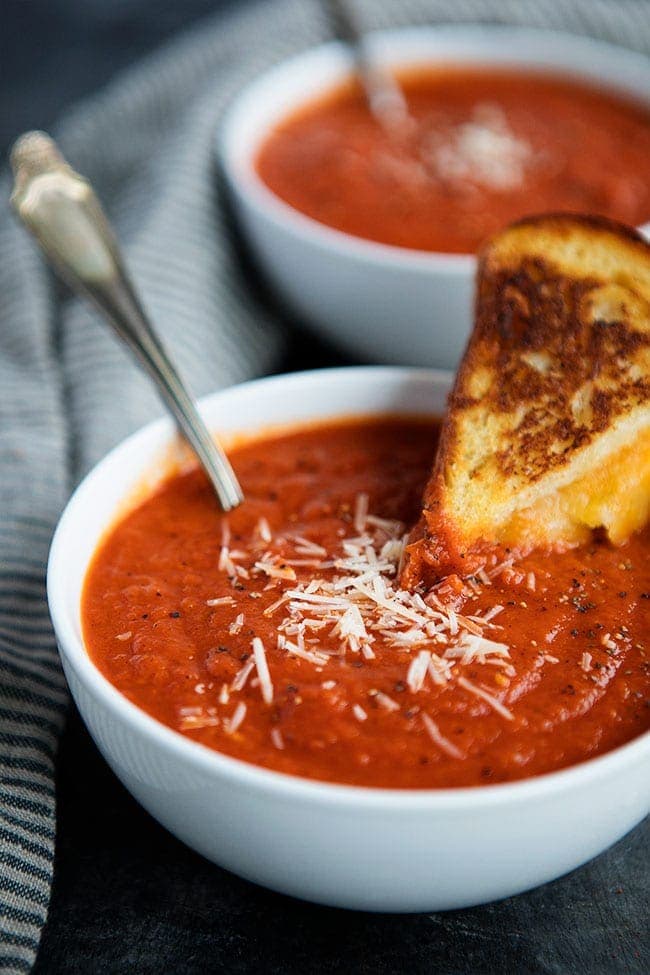
![Smoky Tomato Soup Image]()
-
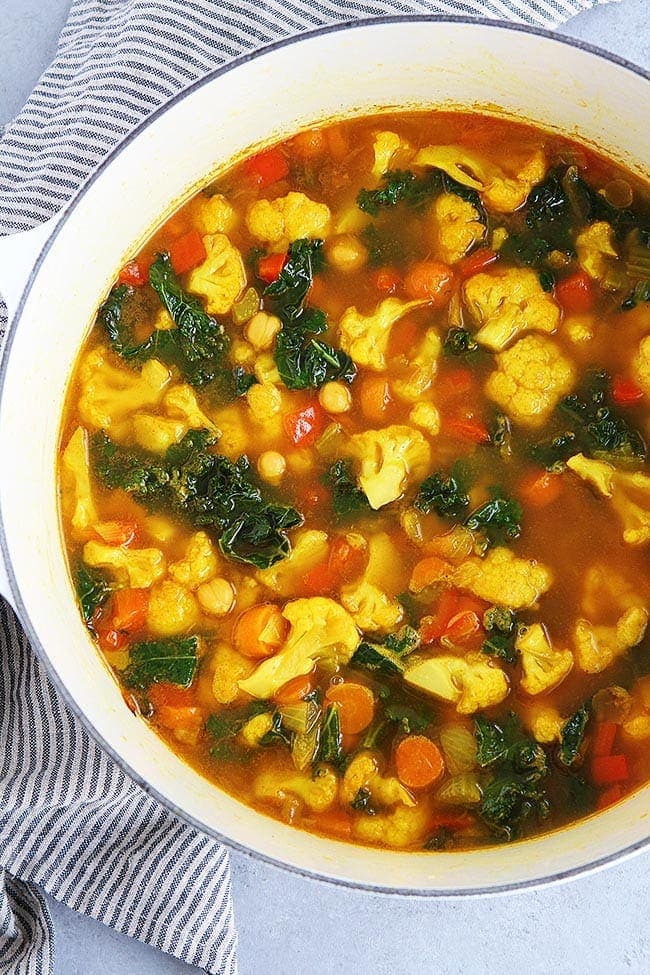
![Turmeric Chickpea Vegetable Soup Image]()
-
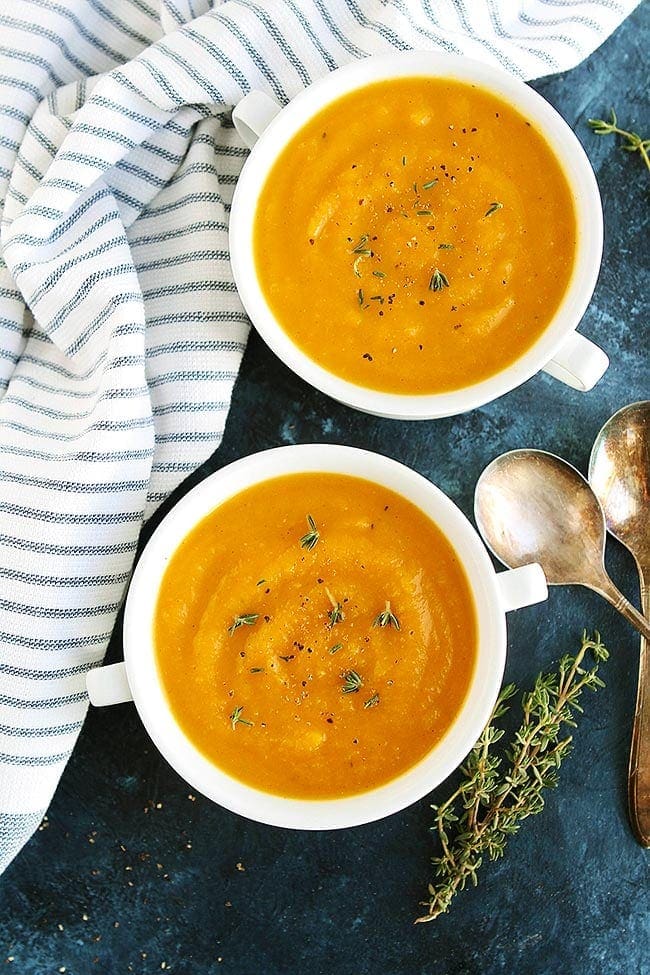
![Easy Butternut Squash Soup Image]()
-
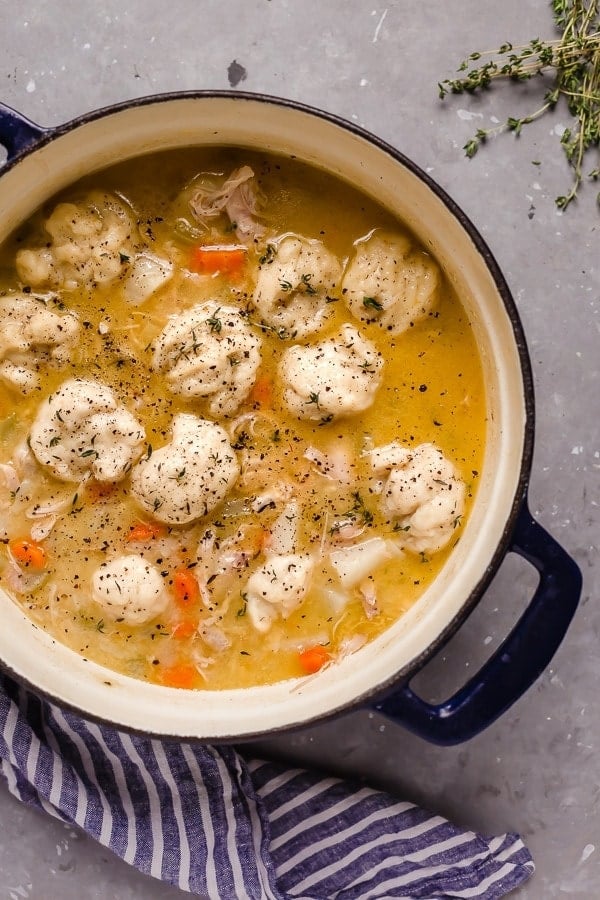
![Chicken and Dumplings Image]()
-
![Slow Cooker Butternut Squash Soup with Maple Roasted Chickpeas Image]()
-
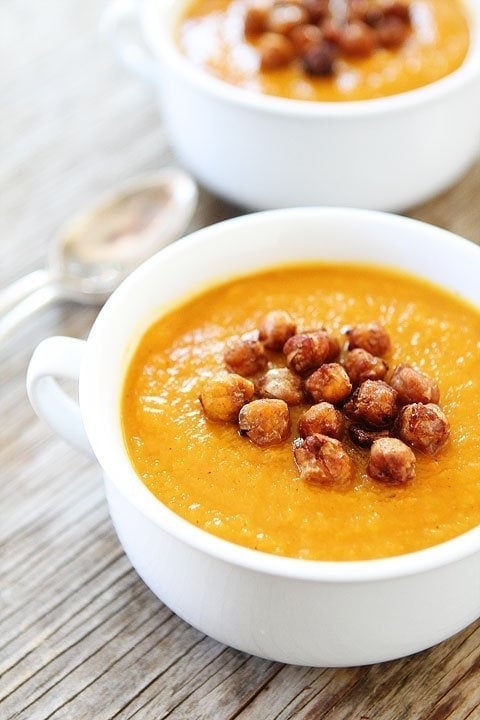
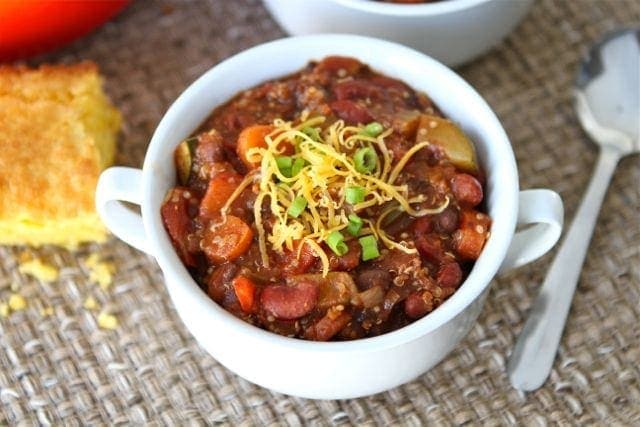
![Vegetarian Quinoa Chili Image]()
-
![Morning Glory Muffins Image]()
-
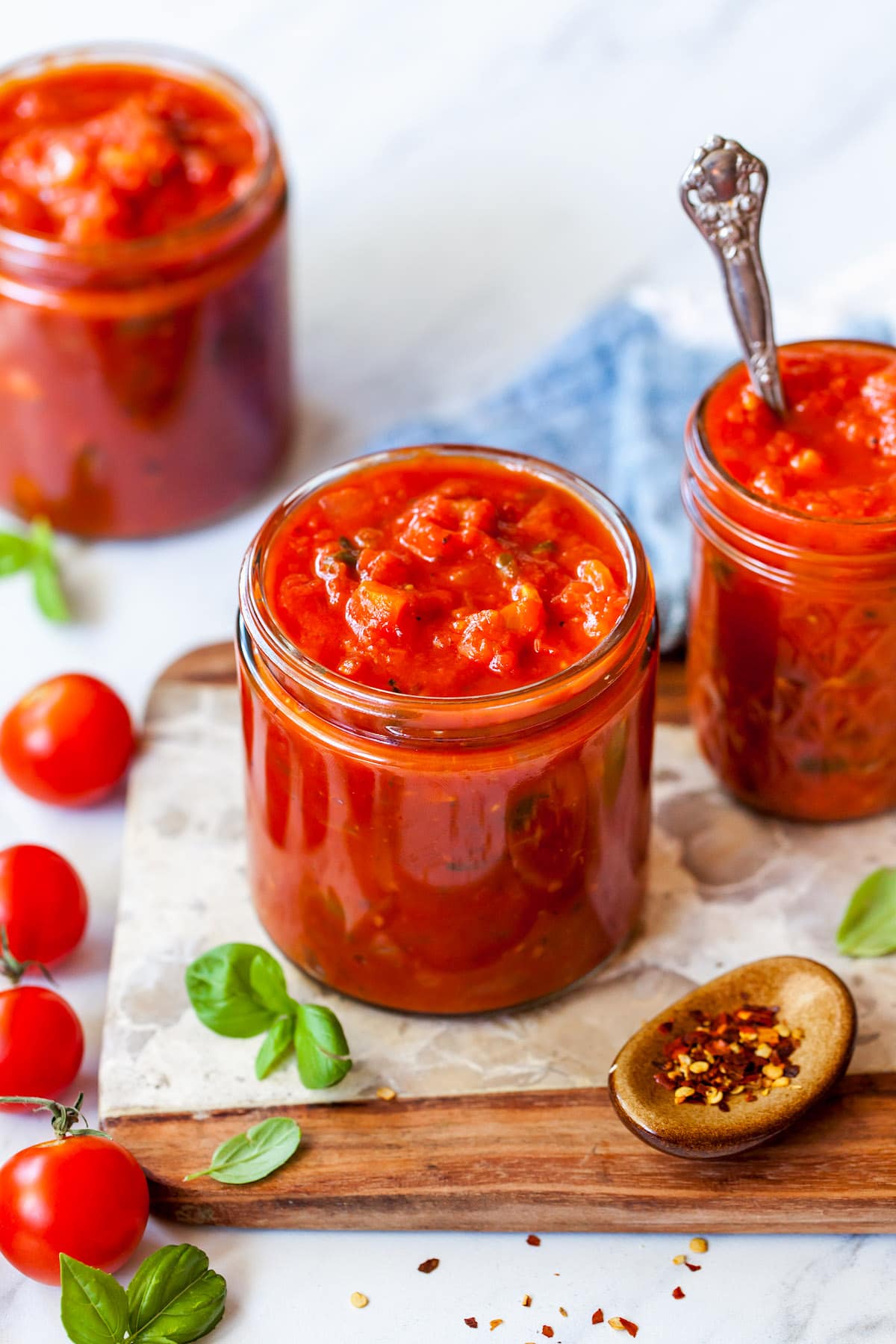
![Easy Marinara Sauce Image]()
-
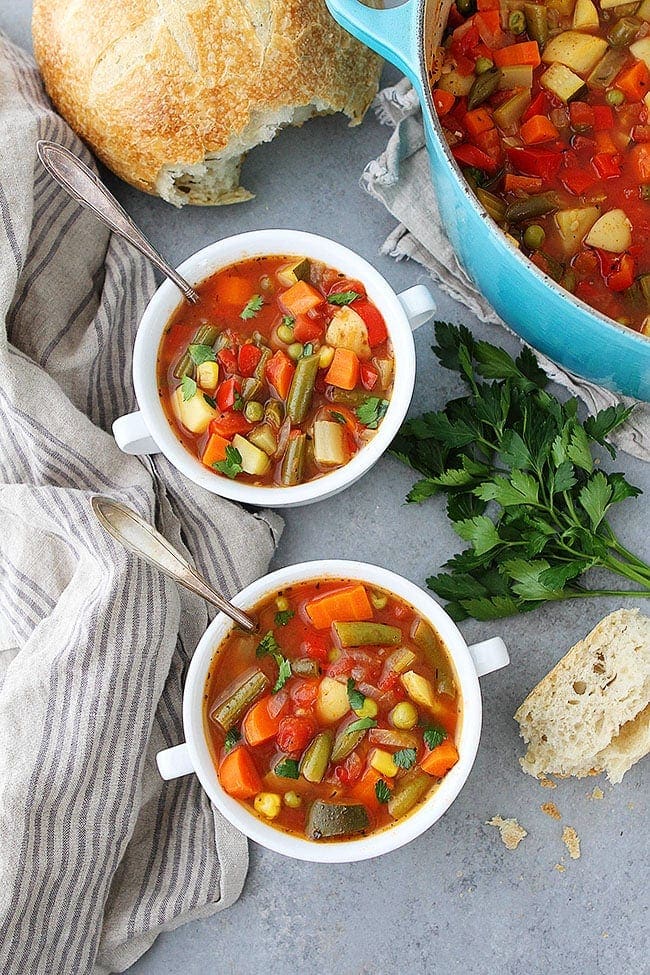
![Vegetable Soup Image]()
-
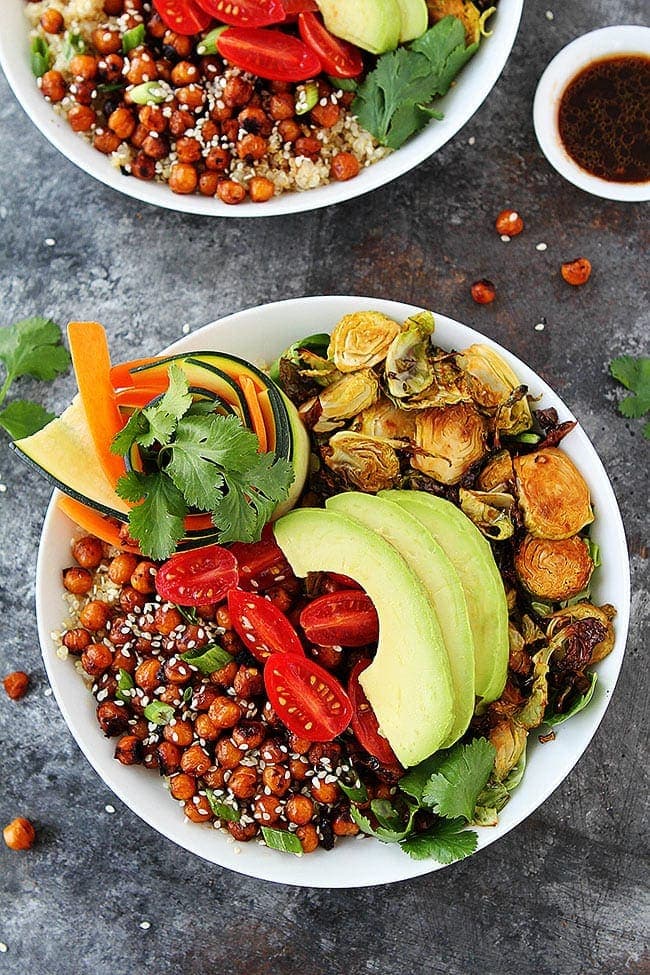
![Korean BBQ Chickpea Bowls Image]()
-
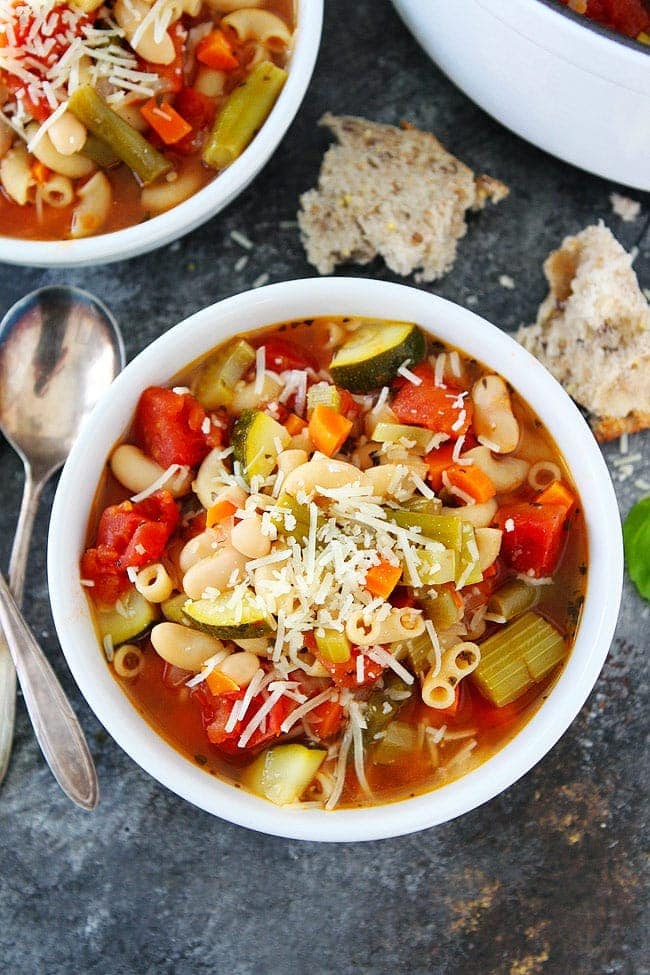
![Minestrone Soup Recipe Image]()
-
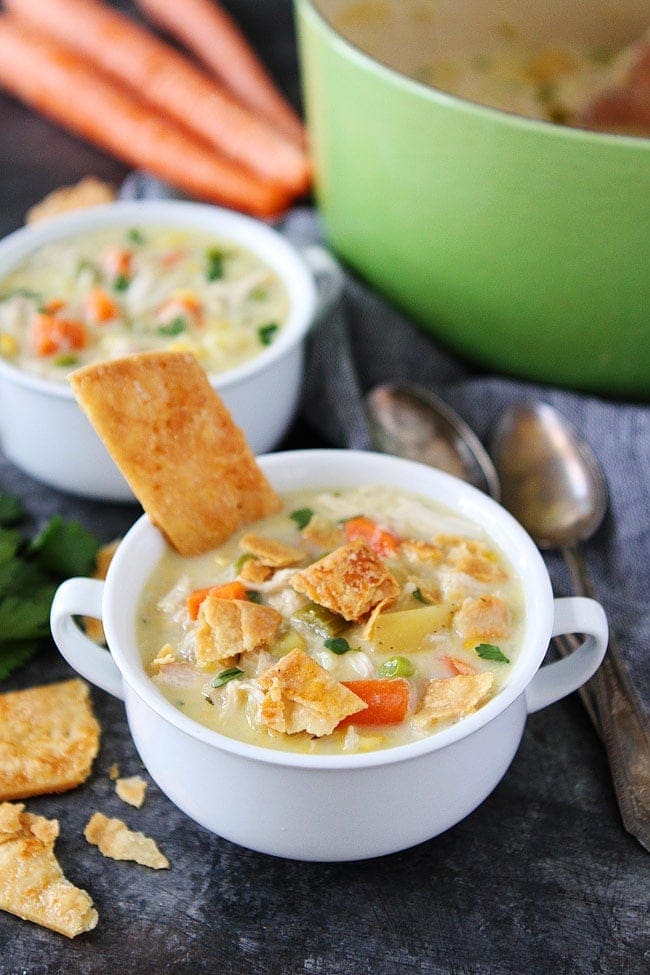
![Chicken Pot Pie Soup Image]()



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__simply_recipes__uploads__2018__04__carrot-top-pesto-horiz-a-1800-a20f3584f09f4d049ec5f6e120975abe.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__serious_eats__seriouseats.com__recipes__images__2013__03__20130320-carrot-cake-ice-cream-1-219b334748e24a4cb17093c6067c7828.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__simply_recipes__uploads__2016__10__2016-10-15-AutumnTabbouleh-13-ccba7dee0e2844ff91d83ba2466f085c.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/20231030-StovetopTzimmesWithCarrotsandRaisins-FredHardy-00-09501800112d4d59bc38a202b08b6009.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Carrotfrieshoriz-767d725ed34145d19f2a99cbd37a9656.jpg)