Mint: Important Facts, Health Benefits, and Recipes
Explore the health benefits, history, and culinary uses of mint, an aromatic herb from the Lamiaceae family, and discover various mint types and recipes.

Nutritional Facts
2 tbsp
Amount per serving
Calories
5
Carbohydrates
1 g
Fat
0.1 g
Protein
0.4 g
Saturated Fat
0 g
Sodium
3.4 mg
Fiber
0.8 g
Best Mint Recipes
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
![Instant Pot Orange Chicken Lettuce Wraps Image]()
-
![Marinated Flank Steak with Asian Chimichurri Sauce Image]()
-
![Soba Noodle With Sriracha Meatballs Image]()
-
![Korean Beef Bulgogi Bowls Recipe Image]()
-
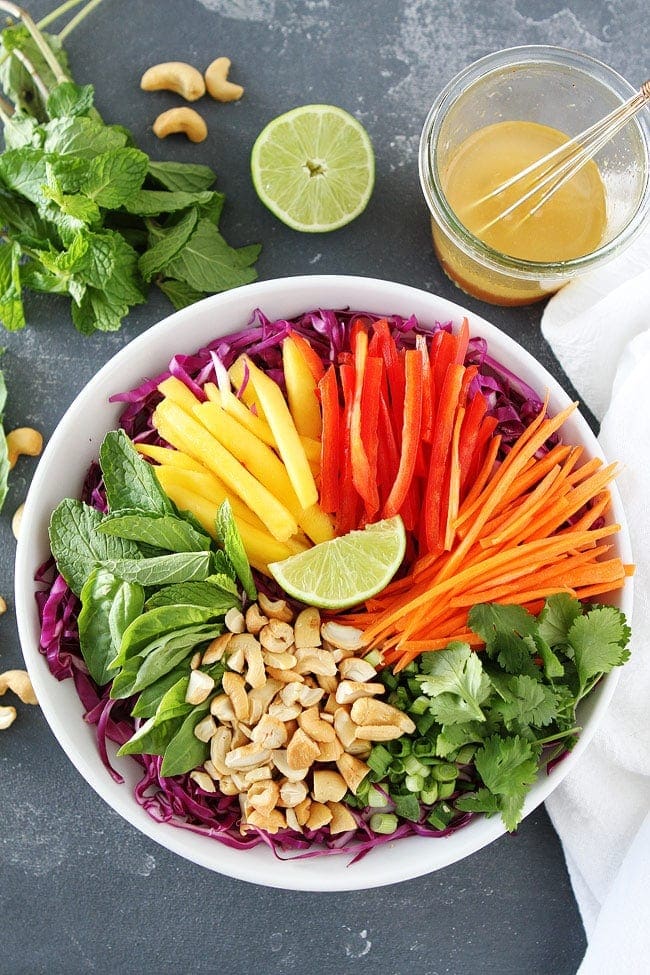
![Thai Zucchini Noodle and Quinoa Salad Image]()
-
![Pomegranate and Orange Champagne Punch Image]()
-
![Champagne Mojitos Image]()
-
![Strawberry and Avocado with Tuna Salad Recipe Image]()
-
![Cheesy Shrimp and Grits Banh Mi in a Waffle Cone Image]()
-
![Vietnamese Grilled Shrimp Spring Rolls Image]()
-
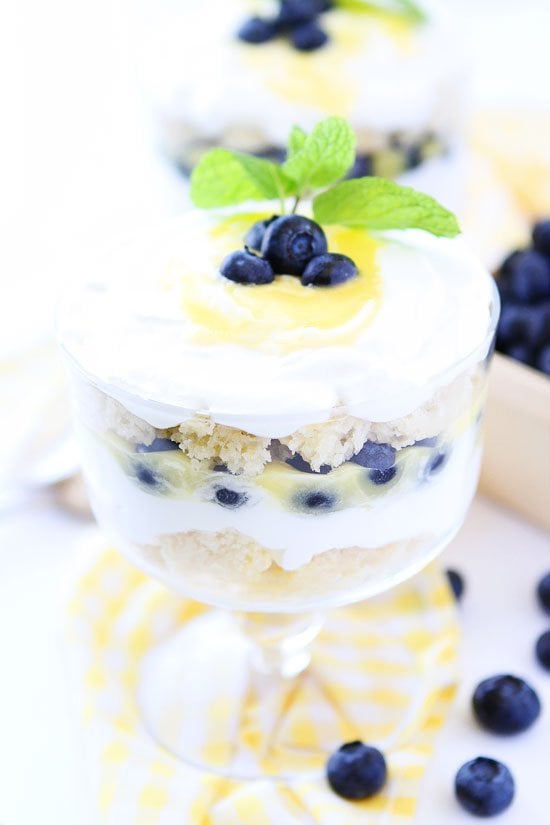
![Berry Tart With Lemon Curd Mascarpone Image]()
-
![Citrus, Fennel and Avocado Salad Image]()
-
![Strawberry and Quinoa Parfait Image]()
-
![Thai Lettuce Wraps Image]()
-
![Pickled Strawberry with Roasted Beet Salad Image]()
-
![Puff Pastry with Sabayon Custard and Strawberries Image]()
-
![Thai Basil Chicken (Pad Krapow Gai) Image]()
-
![Chermoula Image]()
-
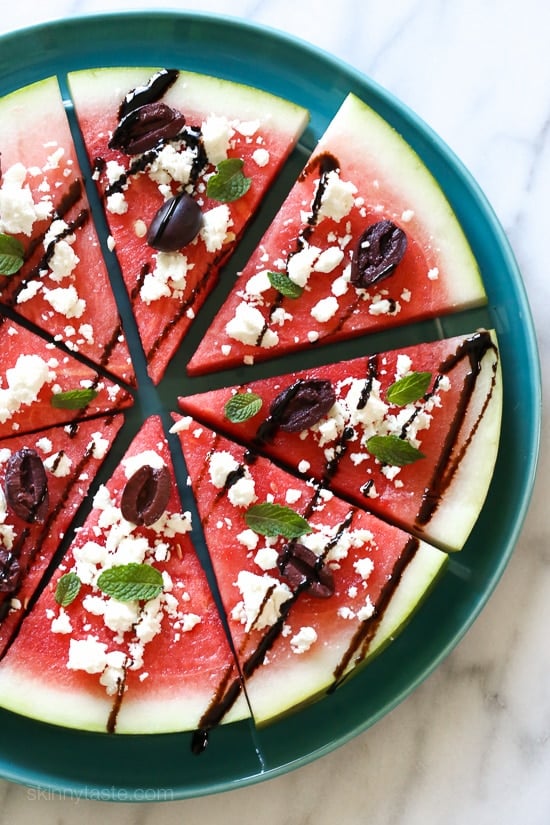
![Watermelon Feta and Balsamic "Pizzas" Image]()
-
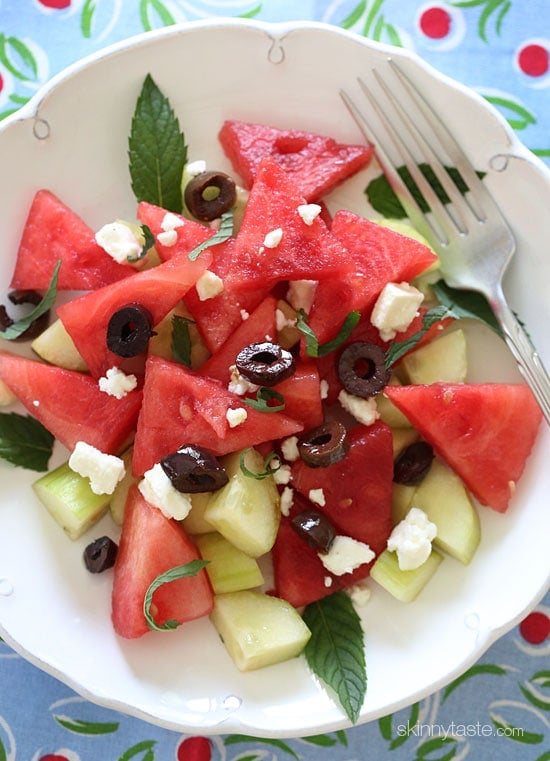
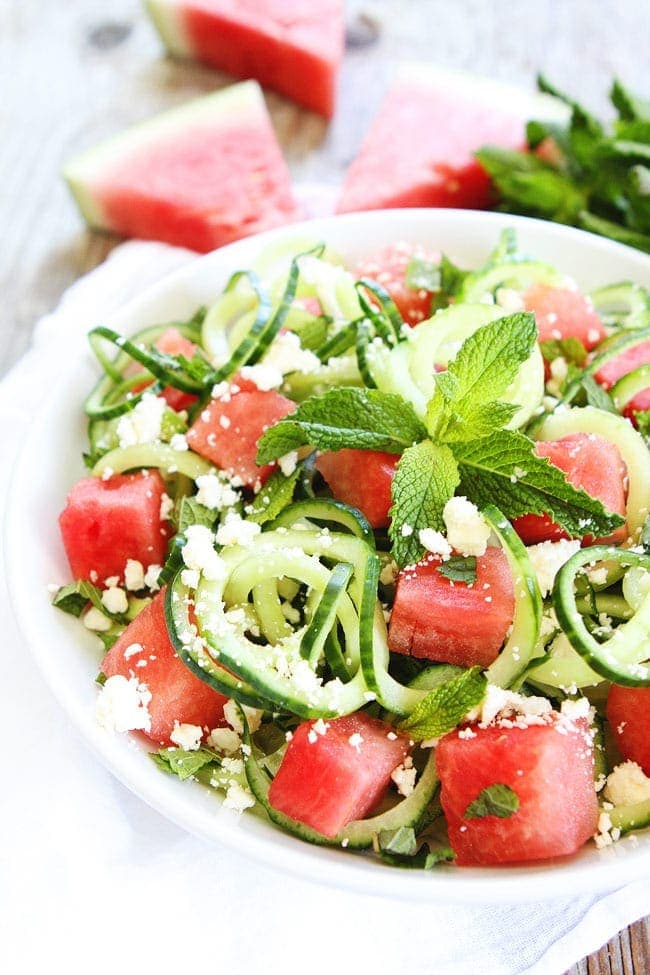
![Watermelon Cucumber Feta Salad Image]()
-
![Teriyaki Pork Bahn Mi Sandwich Image]()
-
![Thai Red Curry Chicken + Video Image]()
-
![Asian Noodle Salad with Shrimp Image]()
-
![Pork Kebabs with Honey Mint Sauce Image]()
-
![Slow Roasted Pork Shoulder Image]()
-
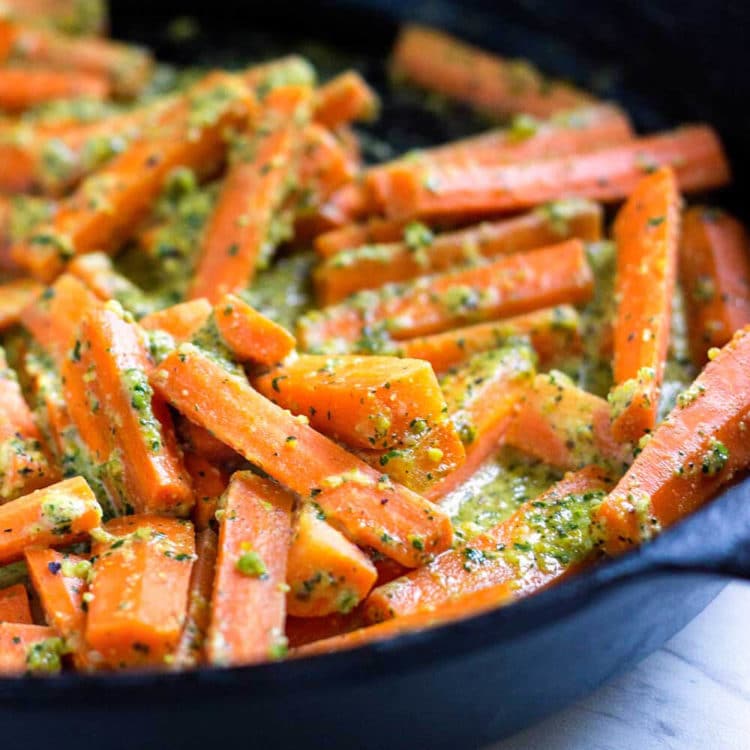
![Carrots with Pistachio Herb Butter Image]()
-
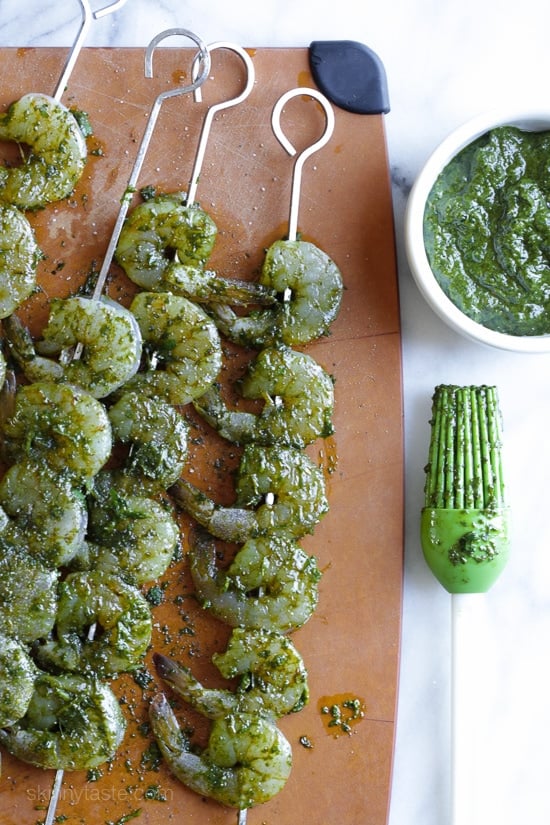
![Watermelon and Grilled Shrimp Skewers Image]()
-
![Corn and Fregola with Grilled Halloumi Cheese Image]()
-
![Grilled Beef and Lamb Kebabs (Kefta) Image]()
-
![Roasted Carrots with Lime and Toasted Cumin Coriander and Fennel Image]()
-
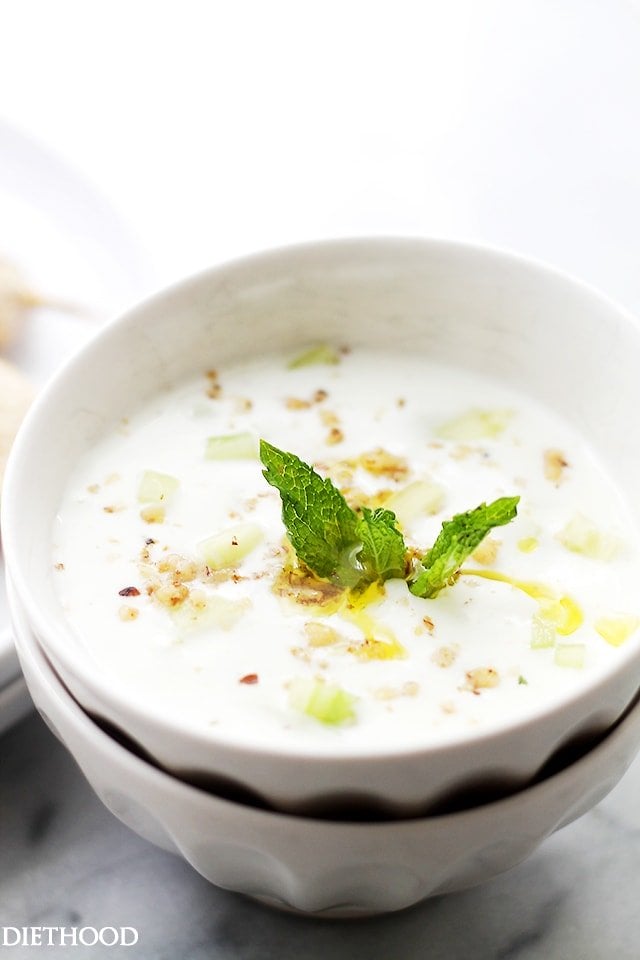
![Authentic Tzatziki Recipe Image]()
-
![Strawberry Pom Mojito Image]()
-
![Blackberry Mint Julep Image]()
-
![Strawberry-Mint Sparkling Limeade Image]()
-
![Cucumber Mojito Image]()
-
![Hibiscus Iced Tea Sparkler Image]()
-
![Citrus Mint Spritzer Image]()
-
![Raspberry Lime Soda Lemonade Image]()
-
![Grilled Peaches with Burrata, Honey, & Pistachios Image]()
-
![Taratur Image]()